Chronic Stress Exposure Alters the Gut Barrier: Sex-Specific Effects on Microbiota and Jejunum Tight Junctions
- PMID: 38306213
- PMCID: PMC10829561
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2023.04.007
Chronic Stress Exposure Alters the Gut Barrier: Sex-Specific Effects on Microbiota and Jejunum Tight Junctions
Abstract
Background: Major depressive disorder (MDD) is the leading cause of disability worldwide. Of individuals with MDD, 30% to 50% are unresponsive to common antidepressants, highlighting untapped causal biological mechanisms. Dysfunction in the microbiota-gut-brain axis has been implicated in MDD pathogenesis. Exposure to chronic stress disrupts blood-brain barrier integrity; still, little is known about intestinal barrier function in these conditions, particularly for the small intestine, where absorption of most foods and drugs takes place.
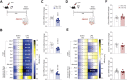
Methods: We investigated how chronic social or variable stress, two mouse models of depression, impact the jejunum intestinal barrier in males and females. Mice were subjected to stress paradigms followed by analysis of gene expression profiles of intestinal barrier-related targets, fecal microbial composition, and blood-based markers.
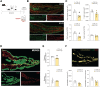
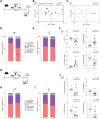
Results: Altered microbial populations and changes in gene expression of jejunum tight junctions were observed depending on the type and duration of stress, with sex-specific effects. We used machine learning to characterize in detail morphological tight junction properties, identifying a cluster of ruffled junctions in stressed animals. Junctional ruffling is associated with inflammation, so we evaluated whether lipopolysaccharide injection recapitulates stress-induced changes in the jejunum and observed profound sex differences. Finally, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, a marker of gut barrier leakiness, was associated with stress vulnerability in mice, and translational value was confirmed on blood samples from women with MDD.
Conclusions: Our results provide evidence that chronic stress disrupts intestinal barrier homeostasis in conjunction with the manifestation of depressive-like behaviors in a sex-specific manner in mice and, possibly, in human depression.
Keywords: Claudins; Cytokines; Sex differences; Social stress; Variable stress.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

