Whole-exome sequencing of pathogenic genes in a family with congenital heart disease: A case report
- PMID: 38306576
- PMCID: PMC10843419
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036977
Whole-exome sequencing of pathogenic genes in a family with congenital heart disease: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common birth defect and an important cause of noninfectious deaths in infants and children. It has high prevalence globally, placing an enormous burden on society and families. Studies of individuals with hereditary or sporadic CHD have provided strong evidence for its genetic basis. The aim of this study was to identify causative gene variants in a Chinese family with congenital heart disease.
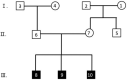
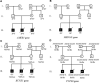
Patient concerns and diagnoses: Three generations of a CHD family were recruited. Proband III.9 was diagnosed with congenital heart disease at age 11 months, and the echocardiogram showed arterial ductus arteriosus, with a left-to-right shunt at the level of the arteries. Precedent III.10 was a twin of Proband III.9 who was diagnosed with congenital heart disease at age 11 months, in whom the echocardiogram revealed an arterial ductus arteriosus, an unenclosed patent ductus arteriosus, and a left to right shunt at the level of the arteries (second figure). III.8 was diagnosed with congenital heart disease at age 15, but echocardiography in this study showed no abnormalities. No cardiac abnormalities were detected in any of his parents, grandparents, or maternal grandparents. We performed whole-exome sequencing on CHD sufferers and their unexpressing family members to investigate the genetic causes of CHD in this family line. Exome sequencing identified 4 mutation sites in this family line. The variant c.3245A>G (p.His1082Arg) of the AMER1 gene was consistent with concomitant X-chromosome recessive inheritance, the variant c.238G>C (p.Val80Leu) of the KCNE1 gene was consistent with autosomal accessory inheritance, and the other 2 variants did not conform to the law of the mode of inheritance of the disease.
Outcomes: The first identified variant, c.3245A>G (p.His1082Arg) of the AMER1 gene, with X-chromosome recessive inheritance, and the variant c.238G>C (p.Val80Leu) of the KCNE1 gene, which has been reported as autosomal dominant, may be the causative agent of CHD in this family line. These findings broaden the genetic scope of congenital heart disease and could help in the development of targeted drugs for the treatment of congenital heart disease.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Shanshan A, Aibin H. Advances in basic research of congenital heart disease. Med J PUMCH. 2021;12:291–7.
-
- Teng Y, You C. Research progress on congenital heart disease caused by cell division cycle genes. J Cardiovasc Pulm Dis. 2021;40:1084–7.
-
- Li S, Jin Y, Yang J, et al. . Advances in the study of the genetic etiology of congenital heart disease. Matern Child Health Care China. 2021;36:2187–91.
-
- Han X, Zhang J, Liu Y, et al. . The lncRNA Hand2os1/Uph locus orchestrates heart development through regulation of precise expression of Hand2. Development. 2019;146:dev176198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

