Mechanical, structural, and physiologic differences between above and below-knee human arteries
- PMID: 38307479
- PMCID: PMC11456514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.01.040
Mechanical, structural, and physiologic differences between above and below-knee human arteries
Abstract
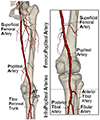
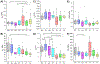
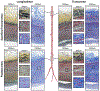
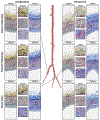
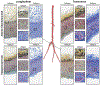
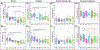
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) affects the lower extremities and frequently results in poor clinical outcomes, especially in the vessels below the knee. Understanding the biomechanical and structural characteristics of these arteries is important for improving treatment efficacy, but mechanical and structural data on tibial vessels remain limited. We compared the superficial femoral (SFA) and popliteal (PA) arteries that comprise the above-knee femoropopliteal (FPA) segment to the infrapopliteal (IPA) anterior tibial (AT), posterior tibial (PT), and fibular (FA) arteries from the same 15 human subjects (average age 52, range 42-67 years, 87 % male). Vessels were imaged using μCT, evaluated with biaxial mechanical testing and constitutive modeling, and assessed for elastin, collagen, smooth muscle cells (SMCs), and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). IPAs were more often diseased or calcified compared to the FPAs. They were also twice smaller, 53 % thinner, and significantly stiffer than the FPA longitudinally, but not circumferentially. IPAs experienced 48 % higher physiologic longitudinal stresses (62 kPa) but 27 % lower circumferential stresses (24 kPa) and similar cardiac cycle stretch of <1.02 compared to the FPA. IPAs had lower longitudinal pre-stretch (1.12) than the FPAs (1.29), but there were no differences in the stored elastic energy during pulsation. The physiologic circumferential stiffness was similar in the above and below-knee arteries (718 kPa vs 754 kPa). Structurally, IPAs had less elastin, collagen, and GAGs than the FPA, but maintained similar SMC content. Our findings contribute to a better understanding of segment-specific human lower extremity artery biomechanics and may inform the development of better medical devices for PAD treatment. STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE: Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) in the lower extremity arteries exhibits distinct characteristics and results in different clinical outcomes when treating arteries above and below the knee. However, their mechanical, structural, and physiologic differences are poorly understood. Our study compared above- and below-knee arteries from the same middle-aged human subjects and demonstrated distinct differences in size, structure, and mechanical properties, leading to variations in their physiological behavior. These insights could pave the way for creating location-specific medical devices and treatments for PAD, offering a more effective approach to its management. Our findings provide new, important perspectives for clinicians, researchers, and medical device developers interested in treating PAD in both above- and below-knee locations.
Keywords: Femoropopliteal artery; Infrapopliteal arteries; Mechanical properties; Structural characteristics; Tibial arteries.
Copyright © 2024 Acta Materialia Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Narula N, Dannenberg AJ, Olin JW, Bhatt DL, Johnson KW, Nadkarni G, Min J, Torii S, Poojary P, Anand SS, Bax JJ, Yusuf S, Virmani R, Narula J, Pathology of peripheral artery disease in patients with critical limb ischemia, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol 72 (2018) 2152–2163, doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mahoney EM, Wang K, Cohen DJ, Hirsch AT, Alberts MJ, Eagle K, Mosse F, Jackson JD, Steg PG, Bhatt DL, One-year costs in patients with a history of or at risk for atherothrombosis in the United States, Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 1 (2008) 38–45, doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.108.775247. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

