The immunology of type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 38308004
- PMCID: PMC7616056
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-023-00985-4
The immunology of type 1 diabetes
Abstract
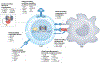
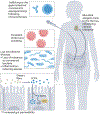
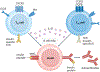
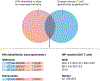
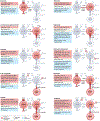
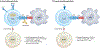
Following the seminal discovery of insulin a century ago, treatment of individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D) has been largely restricted to efforts to monitor and treat metabolic glucose dysregulation. The recent regulatory approval of the first immunotherapy that targets T cells as a means to delay the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic β-cells highlights the critical role of the immune system in disease pathogenesis and tends to pave the way for other immune-targeted interventions for T1D. Improving the efficacy of such interventions across the natural history of the disease will probably require a more detailed understanding of the immunobiology of T1D, as well as technologies to monitor residual β-cell mass and function. Here we provide an overview of the immune mechanisms that underpin the pathogenesis of T1D, with a particular emphasis on T cells.
© 2024. Springer Nature Limited.
Figures

References
-
- Gregory GA et al. Global incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes in 2021 with projection to 2040: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 10, 741–760 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DK129523/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI042288/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA227473/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI166387/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 DK122638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI155387/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 22931/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- P50 CA121974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 20/0006172/DUK_/Diabetes UK/United Kingdom
- U01 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057846/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA215110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N001435/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S009140/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 220772/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK106191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R34 AI155317/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK122638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

