Value of radiological depth of invasion in non-pT4 Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: implication for preoperative MR T-staging
- PMID: 38308013
- PMCID: PMC11364799
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-024-10598-7
Value of radiological depth of invasion in non-pT4 Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: implication for preoperative MR T-staging
Abstract
Objective: The prognostic stratification for oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma (OTSCC) is heavily based on postoperative pathological depth of invasion (pDOI). This study aims to propose a preoperative MR T-staging system based on tumor size for non-pT4 OTSCC.
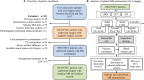
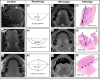
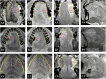
Methods: Retrospectively, 280 patients with biopsy-confirmed, non-metastatic, pT1-3 OTSCC, treated between January 2010 and December 2017, were evaluated. Multiple MR sequences, including axial T2-weighted imaging (WI), unenhanced T1WI, and axial, fat-suppressed coronal, and sagittal contrast-enhanced (CE) T1WI, were utilized to measure radiological depth of invasion (rDOI), tumor thickness, and largest diameter. Intra-class correlation (ICC) and univariate and multivariate analyses were used to evaluate measurement reproducibility, and factors' significance, respectively. Cutoff values were established using an exhaustive method.
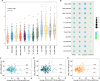
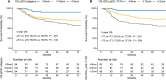
Results: Intra-observer (ICC = 0.81-0.94) and inter-observer (ICC = 0.79-0.90) reliability were excellent for rDOI measurements, and all measurements were significantly associated with overall survival (OS) (all p < .001). Measuring the rDOI on axial CE-T1WI with cutoffs of 8 mm and 12 mm yielded an optimal MR T-staging system for rT1-3 disease (5-year OS of rT1 vs rT2 vs rT3: 94.0% vs 72.8% vs 57.5%). Using multivariate analyses, the proposed T-staging exhibited increasingly worse OS (hazard ratio of rT2 and rT3 versus rT1, 3.56 [1.35-9.6], p = .011; 4.33 [1.59-11.74], p = .004; respectively), which outperformed pathological T-staging based on nonoverlapping Kaplan-Meier curves and improved C-index (0.682 vs. 0.639, p < .001).
Conclusions: rDOI is a critical predictor of OTSCC mortality and facilitates preoperative prognostic stratification, which should be considered in future oral subsite MR T-staging.
Clinical relevance statement: Utilizing axial CE-T1WI, an MR T-staging system for non-pT4 OTSCC was developed by employing rDOI measurement with optimal thresholds of 8 mm and 12 mm, which is comparable with pathological staging and merits consideration in future preoperative oral subsite planning.
Key points: • Tumor morphology, measuring sequences, and observers could impact MR-derived measurements and compromise the consistency with histology. • MR-derived measurements, including radiological depth of invasion (rDOI), tumor thickness, and largest diameter, have a prognostic impact on OS (all p < .001). • rDOI with cutoffs of 8 mm and 12 mm on axial CE-T1WI is an optimal predictor of OS and could facilitate risk stratification in non-pT4 OTSCC disease.
Keywords: Depth of invasion; Magnetic resonance imaging; Squamous cell carcinoma; Tongue cancer; Tumor thickness.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of radiological T category using conventional MRI in patients with oral tongue cancer: comparison with pathological T category.Neuroradiology. 2024 Jun;66(6):907-917. doi: 10.1007/s00234-024-03345-8. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Neuroradiology. 2024. PMID: 38607437 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of tumor depth in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma with multiparametric MRI: correlation with pathology.Eur Radiol. 2022 Jan;32(1):254-261. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08148-6. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34255162 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging for Evaluating the Depth of Invasion in Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2025 Apr 1;24(2):210-219. doi: 10.2463/mrms.mp.2023-0137. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 38447989 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic role of the pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and tumor depth of invasion (DOI) in early-stage squamous cell carcinomas of the oral tongue.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022 Mar;26(1):21-32. doi: 10.1007/s10006-021-00969-5. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022. PMID: 34106358 Review.
-
Correlation between radiologic depth of invasion and pathologic depth of invasion in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Oral Oncol. 2023 Jan;136:106249. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.106249. Epub 2022 Nov 20. Oral Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36417807
References
-
- International Consortium for Outcome Research (ICOR) in Head and Neck Cancer, Ebrahimi A, Gil Z et al (2014) Primary tumor staging for oral cancer and a proposed modification incorporating depth of invasion: an international multicenter retrospective study. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140:1138–1148 - PubMed
-
- Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F et al (2017) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th edn. Springer, New York
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

