Real-world effectiveness of Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies compared to OnabotulinumtoxinA (RAMO) in chronic migraine: a retrospective, observational, multicenter, cohort study
- PMID: 38308209
- PMCID: PMC10836018
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-024-01721-6
Real-world effectiveness of Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies compared to OnabotulinumtoxinA (RAMO) in chronic migraine: a retrospective, observational, multicenter, cohort study
Abstract
Background: Chronic migraine (CM) is a disabling condition with high prevalence in the general population. Until the recent approval of monoclonal antibodies targeting the calcitonin gene-related peptide (Anti-CGRP mAbs), OnabotulinumtoxinA (BoNT-A) was the only treatment specifically approved for CM prophylaxis. Direct comparisons between the two treatments are not available so far.
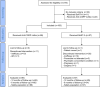
Methods: We performed an observational, retrospective, multicenter study in Italy to compare the real-world effectiveness of Anti-CGRP mAbs and BoNT-A. Patients with CM who had received either treatment according to Italian prescribing regulations were extracted from available clinical databases. Efficacy outcomes included the change from baseline in monthly headache days (MHD), MIgraine Disability ASsessment test (MIDAS), and monthly acute medications (MAM) evaluated at 6 and 12 months of follow-up. The primary outcome was MHD change from baseline at 12 months. Safety outcomes included serious adverse events (SAE) and treatment discontinuation. Unadjusted and adjusted models were used for the analyses.
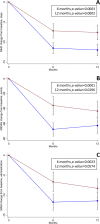
Results: Two hundred sixteen potentially eligible patients were screened; 183 (86 Anti-CGRP mAbs; 97 BoNT-A) were included. One hundred seventy-one (80 Anti-CGRP mAbs; 91 BoNT-A) and 154 (69 Anti-CGRP mAbs; 85 BoNT-A) patients were included in the efficacy analysis at 6 and 12 months of follow-up, respectively. Anti-CGRP mAbs and BoNT-A both resulted in a mean MHD reduction at 6 (-11.5 and -7.2 days, respectively; unadjusted mean difference -4.3; 95%CI -6.6 to -2.0; p = 0.0003) and 12 months (-11.9 and -7.6, respectively; unadjusted mean difference -4.4; 95%CI -6.8 to -2.0; p = 0.0002) of follow-up. Similar results were observed after adjusting for baseline confounders. Anti-CGRP mAbs showed a significant MIDAS (-31.7 and -19.2 points, p = 0.0001 and p = 0.0296, respectively) and MAM reduction (-5.1 and -3.1 administrations, p = 0.0023 and p = 0.0574, respectively) compared to BoNT-A at 6 and 12 months. No SAEs were reported. One patient receiving fremanezumab discontinued treatment due to arthralgia. Treatment discontinuations, mainly for inefficacy, were comparable.
Conclusion: Both Anti-CGRP mAbs and BoNT-A were effective in CM patients with Anti-CGRP mAbs presenting higher effect magnitude, with comparable safety. Still, BoNT-A remains a valuable option for CM patients with contraindications to Anti-CGRP mAbs or for frail categories who are candidates to local therapy with limited risk of systemic administration.
Keywords: Erenumab; Fremanezumab; Galcanezumab; Migraine; Onabotulinumtoxin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Licia Grazzi received consultancy and advisory fees from Abbvie, Eli-Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis AG, Pfizer, and TEVA Pharm Ind. Riccardo Giossi received support for congress participation from Mylan and acted as a consultant for Daiichi-Sankyo, outside this work. Claudia Altamura is associated editor for Frontiers of Human Neuroscience and received travel grants and/or personal fees for advisory boards and speaker panels, from Novartis, Eli-Lilly, Lundbeck, Teva, Lusofarmaco, Laborest, Abbvie/Allergan, Almirall, and Pfizer. Fabrizio Vernieri received travel grants, honoraria for advisory boards, speaker panels, or clinical investigation studies from Abbvie/Allergan, Amgen, Angelini, Eli-Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Teva. Other Authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Y-Y, Ye X-Q, Tang T-C, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies Versus Botulinum Neurotoxin a in the Preventive treatment of chronic migraine: an adjusted Indirect Treatment Comparison Meta-Analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:671845. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.671845. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

