Nursing experience and leadership skills among staff nurses and intern nursing students in Saudi Arabia: a mixed methods study
- PMID: 38308273
- PMCID: PMC10835976
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-024-01750-1
Nursing experience and leadership skills among staff nurses and intern nursing students in Saudi Arabia: a mixed methods study
Abstract
Background: Nurse leaders have a crucial impact in healthcare settings. Hospitals require qualified nurses with leadership skills to provide healthy work environments and enhance the outcomes related to staff nurses and patients. This study aimed to investigate the effect of nursing experience on leadership skills among staff nurses and intern nursing students.
Methods: A mixed methods design was applied (quantitative survey design for quantitative part and open-ended questions for qualitative part). Convenience sampling of staff nurses and intern nursing students in Saudi Arabia was applied. There were148 participants who completed the survey of the quantitative part, and 50 of them completed the qualitative part. Participants completed the Leadership Practice Inventory Questionnaire. SPSS v26 was used to analyze quantitative part, and thematic analysis was used to analyze qualitative part.
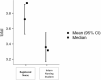
Results: This study found a significance difference among participating groups regarding to the years of experience (F = 5.05, p = 0.00). Three themes were found for the qualitative part which were strategies to enhance leadership skills, factors affecting leadership skills, and obstacles facing participants related to leadership skills. The qualitative data also revealed that participants found that clinical supervision and education ways to enhance the leadership skills, while work pressure, work environment and communication were obstacles of developing their leadership skills.
Conclusion: Leadership skills are considered as a significant component of the function of qualified nurses and should be viewed as central to intern nursing students' learning development. Moreover, leadership skills are essential for the patient and organization outcomes. Nursing colleges and educators play an important role in enhancing to leadership skills as well as experience. Nurse leaders can create healthy care environments that have high quality and safety for patients. Management systems in healthcare organizations must motivate and support clinical leaders who can recognize both individual and clinical requirements and address current issues in their field.
Keywords: Experience; Intern; Leadership; Nurses; Qualitative; Quantitative; Skills; Student.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Gopee N, Galloway J. Leadership and management in healthcare. Sage; 2017 Mar. p. 6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources