Targeting AXL induces tumor-intrinsic immunogenic response in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant liver cancer
- PMID: 38310091
- PMCID: PMC10838288
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06493-0
Targeting AXL induces tumor-intrinsic immunogenic response in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant liver cancer
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive malignancy without effective therapeutic approaches. Here, we evaluate the tumor-intrinsic mechanisms that attenuate the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) that is observed in patients with advanced HCC who progress on first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy. Upregulation of AXL observed in sorafenib- and lenvatinib-resistant HCCs is correlated with poor response towards TKI and ICI treatments. AXL upregulation protects sorafenib-resistant HCC cells from oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, and accompanying immunogenic cell death through suppressed tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and STING-type I interferon pathways. Pharmacological inhibition of AXL abrogates the protective effect and re-sensitizes TKI-resistant HCC tumors to anti-PD-1 treatment. We suggest that targeting AXL in combination with anti-PD-1 may provide an alternative treatment scheme for HCC patients who progress on TKI treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
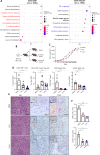
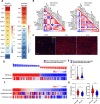
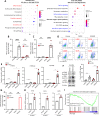

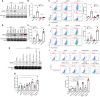
References
-
- Haas L, Elewaut A, Gerard CL, Umkehrer C, Leiendecker L, Pedersen M, et al. Acquired resistance to anti-MAPK targeted therapy confers an immune-evasive tumor microenvironment and cross-resistance to immunotherapy in melanoma. Nat Cancer. 2021;2:693–708. doi: 10.1038/s43018-021-00221-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

