An analysis of direct and indirect costs in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- PMID: 38312251
- PMCID: PMC10831557
- DOI: 10.1002/ski2.306
An analysis of direct and indirect costs in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Abstract
Background: Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with recurrent nodules and abscesses that culminate in purulent discharge and scarring. It has significant physical, psychological and financial impact.
Objectives: This study plans to analyse patient costs associated with HS. Direct costs include prescription items. Indirect or out-of-pocket costs include dressings, analgesia, and healthcare-related travel costs. This study will also assess disease impact on quality-of-life (QOL).
Methods: Patients with HS diagnosis attending dermatology OPD at our public tertiary centre were invited to participate. Ethical approval was secured, and informed consent was obtained. Participants completed an anonymous survey which was analysed to identify costs associated with HS as well as demographics and QOL impact.
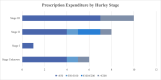
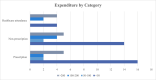
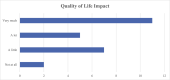
Results: A total of 25 patients completed the survey; median age was 29% and 80% were female. Median time from HS onset to diagnosis was 2 years, with 24% waiting >10 years to be diagnosed. In the past 3 months, 20% spent >€200 in both categories; prescription and non-prescription items. In the non-prescription category, 36% of patients reported expenditure >€100 in the past 3 months. Dressings were the most common out-of-pocket expense (in 15/25 patients), followed by analgesia and protective clothing. Attendance at medical appointments cost 24% of patients €50-€200. Four participants reported difficulty accessing HS treatments due to associated costs. Mean number of absence days from work/education as result of HS was 8.7 in the past 3 months. Two patients reported being on disability allowance, and two on unemployment benefit as result of their skin disorder. In the QOL question; 96% reported disease impact on QOL, and 11 participants reported that it affected their life 'very much'.
Conclusions: HS is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with significant financial burden alongside the well-analysed biopsychosocial disease impact. Financial burden can be divided into direct prescription costs and indirect costs such as non-prescription items, protective clothing and travel costs which we have explored in this study. Further research is needed in this area to identify and optimise both the financial and QOL implications of HS in acute flares and chronic disease management.
© 2023 The Authors. Skin Health and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Two Cases of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treated with Adalimumab at the Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Clinical Hospital Mostar.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021 Jul;29(2):108-110. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2021. PMID: 34477078
-
Pain experiences among those living with hidradenitis suppurativa: a qualitative study.Br J Dermatol. 2023 Jan 23;188(1):41-51. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljac018. Br J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36689519
-
Profound consequences of hidradenitis suppurativa: a review.Br J Dermatol. 2020 Dec;183(6):e171-e177. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16603. Epub 2018 May 9. Br J Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 29744872 Review.
-
Unmet clinical needs and burden of disease in hidradenitis suppurativa: real-world experience from EU5 and US.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022 Sep;36(9):1597-1605. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18163. Epub 2022 May 9. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022. PMID: 35445469 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-based approach to the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa, based on the European guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016 Sep;17(3):343-351. doi: 10.1007/s11154-016-9328-5. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2016. PMID: 26831295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Management and Burden of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: An Italian Hybrid Real-World Study.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025 Jul;15(7):1771-1785. doi: 10.1007/s13555-025-01407-0. Epub 2025 May 9. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40343666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Citizens Information . Health > Medical Cards. 2023. https://www.citizensinformation.ie/en/health/
-
- Onderdijk AJ, Van Der Zee HH, Esmann S, Lophaven S, Dufour DN, Jemec GBE. Depression in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;473–478. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
