Machine learning-based approach for automated classification of cell and extracellular matrix using nanomechanical properties
- PMID: 38312803
- PMCID: PMC10835007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100970
Machine learning-based approach for automated classification of cell and extracellular matrix using nanomechanical properties
Abstract
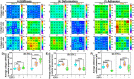
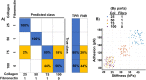
Fibrosis characterized by excess accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) due to complex cell-ECM interactions plays a pivotal role in pathogenesis. Herein, we employ the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) model to investigate dynamic alterations in nanomechanical attributes arising from the cell-ECM interactions to study the fibrosis paradigm. Several segregated studies performed on cellular and ECM components fail to recapitulate their complex collaboration. We utilized collagen and fibronectin, the two most abundant PDAC ECM components, and studied their nanomechanical attributes. We demonstrate alteration in morphology and nanomechanical attributes of collagen with varying thicknesses of collagen gel. Furthermore, by mixing collagen and fibronectin in various stoichiometry, their nanomechanical attributes were observed to vary. To demonstrate the dynamicity and complexity of cell-ECM, we utilized Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells with or without collagen. We observed that Panc-1 and AsPC-1 cells interact differently with collagen and vice versa, evident from their alteration in nanomechanical properties. Further, using nanomechanics data, we demonstrate that ML-based techniques were able to classify between ECM as well as cell, and cell subtypes in the presence/absence of collagen with higher accuracy. This work demonstrates a promising avenue to explore other ECM components facilitating deeper insights into tumor microenvironment and fibrosis paradigm.
Keywords: Extracellular matrix; Fibrosis; Machine learning; Nanomechanical attributes; Pancreatic cancer; Support vector machines.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Thannickal V.J., Toews G.B., White E.S., Lynch J.P., Iii, Martinez F.J. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2004;55:395–417. - PubMed
-
- Özdemir B.C., Pentcheva-Hoang T., Carstens J.L., Zheng X., Wu C.-C., Simpson T.R., Laklai H., Sugimoto H., Kahlert C., Novitskiy S.V. Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas cancer with reduced survival. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(6):719–734. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast in wound healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J. Pathol.: A Journal of the Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland. 2003;200(4):500–503. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

