Response to Savolitinib in a Patient with Advanced Poorly Differentiated Lung Carcinoma Positive for a Novel EML4-MET Gene Fusion
- PMID: 38313385
- PMCID: PMC10838107
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S442685
Response to Savolitinib in a Patient with Advanced Poorly Differentiated Lung Carcinoma Positive for a Novel EML4-MET Gene Fusion
Abstract
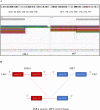
Background: Cellular-mesenchymal to epithelial transition factor (c-MET) alterations have significant therapeutic implications in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Although MET fusion is a rare genomic event, advances in detection technologies have enabled the identification of various MET fusion partner genes. However, standard therapeutic options for MET fusion in NSCLC cases remain undefined. This report presents a novel fusion variant, EML4-MET, encompassing exons 1 to 13 of EML4 and exons 15 to 21 of MET, including the entire MET kinase domain, and discusses the response of this case to savolitinib treatment.
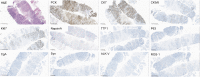
Case presentation: A 65-year-old woman was diagnosed with advanced poorly differentiated lung carcinoma. Molecular profiling of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), carried out by next-generation sequencing (NGS), identified a novel EML4-MET fusion. The patient was administered the MET receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor savolitinib at 400 mg daily. One month later, computed tomography (CT) revealed some lesions with volume reduction. However, COVID-19 diminished the efficacy of savolitinib. Regrettably, the patient succumbed to respiratory and circulatory failure due to disease progression in March 2023.
Conclusion: This case uncovers a new type of MET fusion and expands the range of potential MET fusion targets in NSCLC. The patient responded to savolitinib, suggesting a reference basis for the treatment of similar cases with EML4-MET fusion in the future. Additional research is warranted to assess the biological significance of the EML4-MET fusion in NSCLC.
Keywords: EML4-MET; non-small cell lung cancer; savolitinib.
© 2024 Ouyang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

