Electrochemical HPLC Determination of Piperazine Antihistamine Drugs Employing a Spark-Generated Nickel Oxide Nanoparticle-Modified Carbon Fiber Microelectrode
- PMID: 38313503
- PMCID: PMC10831984
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09474
Electrochemical HPLC Determination of Piperazine Antihistamine Drugs Employing a Spark-Generated Nickel Oxide Nanoparticle-Modified Carbon Fiber Microelectrode
Abstract
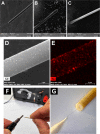
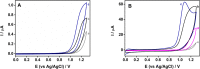
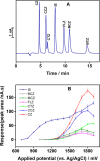
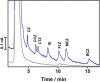
In this work, we demonstrate a sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for the determination of piperazine antihistamine drugs employing innovative electrochemical detection based on a spark-generated nickel oxide nanoparticle-modified carbon fiber microelectrode built into a miniaturized electrochemical detector. The direct carbon fiber-to-nickel plate electrode spark discharge, carried at 0.8 kV DC, with the nickel electrode connected to the negative pole of the high-voltage power supply, provides extremely fast (1 s) in situ tailoring of the carbon fiber microelectrode surface by nickel oxide nanoparticles. It has been found that nickel oxide nanoparticles exhibit an electrocatalytic effect toward the piperazine moiety electrooxidation process, as confirmed by voltammetric experiments, revealing the shift in the peak potential from 1.25 to 1.09 V versus Ag/AgCl. Cetirizine, cyclizine, chlorcyclizine, flunarizine, meclizine, and buclizine were selected as sample piperazine antihistamine drugs, while diclofenac served as an internal standard. The isocratic reversed-phase separation of the above set was achieved within 15 min using an ARION-CN 3 μm column with a binary mobile phase consisting of 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 3) and methanol (45/55, v/v). The limits of detection (LOD) were within the range of 3.8-120 nM (for cyclizine and buclizine) at E = +1500 mV (vs Ag/AgCl), while the response was linear within the concentration range measured up to 5 μmol L-1. The method was successfully applied to the determination of piperazine antihistamine drugs in spiked plasma samples.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mahdy A. M.; Webster N. R. Histamine and antihistamines. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 18 (4), 210–215. 10.1016/j.mpaic.2017.01.007. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
