Unraveling Epigenetic Interplay between Inflammation, Thrombosis, and Immune-Related Disorders through a Network Meta-analysis
- PMID: 38313596
- PMCID: PMC10837039
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2222-9126
Unraveling Epigenetic Interplay between Inflammation, Thrombosis, and Immune-Related Disorders through a Network Meta-analysis
Abstract
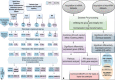
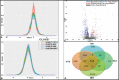
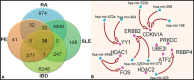
Inflammation and thrombosis are two distinct yet interdependent physiological processes. The inflammation results in the activation of the coagulation system that directs the immune system and its activation, resulting in the initiation of the pathophysiology of thrombosis, a process termed immune-thrombosis. Still, the shared underlying molecular mechanism related to the immune system and coagulation has not yet been explored extensively. Inspired to answer this, we carried out a comprehensive gene expression meta-analysis using publicly available datasets of four diseases, including venous thrombosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. A total of 609 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) shared by all four datasets were identified based on the combined effect size approach. The pathway enrichment analysis of the DEGs showed enrichment of various epigenetic pathways such as histone-modifying enzymes, posttranslational protein modification, chromatin organization, chromatin-modifying enzymes, HATs acetylate proteins. Network-based protein-protein interaction analysis showed epigenetic enzyme coding genes dominating among the top hub genes. The miRNA-interacting partner of the top 10 hub genes was determined. The predomination of epitranscriptomics regulation opens a layout for the meta-analysis of miRNA datasets of the same four diseases. We identified 30 DEmiRs shared by these diseases. There were 9 common DEmiRs selected from the list of miRNA-interacting partners of top 10 hub genes and shared significant DEmiRs from microRNAs dataset acquisition. These common DEmiRs were found to regulate genes involved in epigenetic modulation and indicate a promising epigenetic aspect that needs to be explored for future molecular studies in the context of immunothrombosis and inflammatory disease.
Keywords: epigenetic modulators; hypoxia; inflammation; meta-analysis; miRNA; thrombosis.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

