Immunoinformatics Approach to Design a Chimeric CD70-Peptide Vaccine against Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 38314087
- PMCID: PMC10838208
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/2875635
Immunoinformatics Approach to Design a Chimeric CD70-Peptide Vaccine against Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
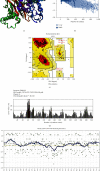
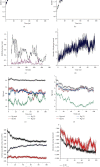
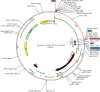
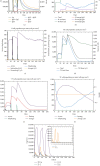
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) accounts for the majority of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Overexpression of CD70 has been linked to advanced stages of RCC. Therefore, this study aims to develop a multiepitope vaccine targeting the overexpressed CD70 using immunoinformatics techniques. In this investigation, in silico multiepitope vaccines were constructed by linking specific CD70 protein epitopes for helper T lymphocytes and CD8+ T lymphocytes. To enhance immunogenicity, sequences of cell-penetrating peptide (CPP), penetratin (pAntp), along with the entire sequence of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), were attached to the N-terminal and C-terminal of the CD70 epitopes. Computational assessments were performed on these chimeric vaccines for antigenicity, allergenicity, peptide toxicity, population coverage, and physicochemical properties. Furthermore, refined 3D constructs were subjected to a range of analyses, encompassing structural B-cell epitope prediction and molecular docking. The chosen vaccine construct underwent diverse assessments such as molecular dynamics simulation, immune response simulation, and in silico cloning. All vaccines comprised antigenic, nontoxic, and nonallergenic epitopes, ensuring extensive global population coverage. The vaccine constructs demonstrated favorable physicochemical characteristics. The binding affinity of chimeric vaccines to the TNF receptor remained relatively stable, influenced by the alignment of vaccine components. Molecular docking and dynamics analyses predicted stable interactions between CD70-CPP-TNF and the TNF receptor, indicating potential efficacy. In silico codon optimization and cloning of the vaccine nucleic acid sequence were accomplished using the pET28a plasmid. Furthermore, this vaccine displayed the capacity to modulate humoral and cellular immune responses. Overall, the results suggest therapeutic potential for the chimeric CD70-CPP-TNF vaccine against RCC. However, validation through in vitro and in vivo experiments is necessary. This trial is registered with NCT04696731 and NCT04046445.
Copyright © 2024 Haideh Namdari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prioritization of potential vaccine candidates and designing a multiepitope-based subunit vaccine against multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhi str. CT18: A subtractive proteomics and immunoinformatics approach.Microb Pathog. 2021 Oct;159:105150. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105150. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34425197
-
Immunoinformatics Approach to Design Novel Subunit Vaccine against the Epstein-Barr Virus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0115122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01151-22. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36094198 Free PMC article.
-
3CL hydrolase-based multiepitope peptide vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 using immunoinformatics.J Med Virol. 2020 Oct;92(10):2114-2123. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25993. Epub 2020 May 22. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32379348
-
Multi-epitopevaccines, from design to expression; an in silico approach.Hum Immunol. 2024 May;85(3):110804. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2024.110804. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Hum Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38658216 Review.
-
CD70: An Emerging Anticancer Target in Renal Cell Carcinoma and Beyond.Annu Rev Med. 2025 Jan;76(1):257-266. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-070623-045906. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Annu Rev Med. 2025. PMID: 39570653 Review.
Cited by
-
CD70: An emerging target for integrated cancer diagnosis and therapy.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Jul;15(7):e70400. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70400. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40629902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Junker K., Hindermann W., von Eggeling F., Diegmann J., Haessler K., Schubert J. CD70: a new tumor specific biomarker for renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Urology . 2005;173(6):2150–2153. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000158121.49085.ba. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bleumer I., Tiemessen D. M., Oosterwijk-Wakka J. C., et al. Preliminary analysis of patients with progressive renal cell carcinoma vaccinated with CA9-peptide-pulsed mature dendritic cells. Journal of Immunotherapy . 2007;30(1):116–122. doi: 10.1097/01.cji.0000211318.22902.ec. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

