Zinc-Boron Complex-Based Dietary Supplements for Longevity and Healthy Life
- PMID: 38314211
- PMCID: PMC10832868
- DOI: 10.12865/CHSJ.49.03.10
Zinc-Boron Complex-Based Dietary Supplements for Longevity and Healthy Life
Abstract
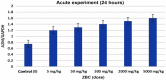
The nutritional role of zinc (Zn) and boron (B) in the plant-animal-human food chain is highly topical worldwide research. Our data indicated that Zn-B complex (ZBC)-based dietary supplements can be used as stable non-toxic formulations, with high intestinal absorption rate, inducing alpha2-macroglobulin (A2M) expression for longevity and healthy life. ZBC is metabolized by hydrolysis, mainly at the absorption site (intestinal level), and most of it is excreted in the urine. Within seven hours from the administration in mice, almost the entire amount of orally absorbed ZBC is eliminated in a metabolized form. The highest amount of A2M protein in mouse liver was determined by immunoabsorbance assay in the chronic experiment (1000mg/kg of ZBC), followed by the subchronic experiment (at the same dose of ZBC), and by the acute experiment (5000mg/kg of ZBC).
Keywords: A2M protein; dietary supplement; healthy life; longevity; zinc-boron complex.
Copyright © 2023, Medical University Publishing House Craiova.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Sharma S, Ebadi M. Significance of metallothioneins in aging brain. Neurochem Int. 2014;65:40–48. - PubMed
-
- Werynska B, Pula B, Kobierzycki C, Dziegiel P, Podhorska-Okolow M. Metallothioneins in the lung cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2015;53(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Andreini C, Banci L, Bertini I, Rosato A. Zinc through the three domains of life. J Proteome Res. 2006;5(11):3173–3178. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
