Morphogenesis of fungiform papillae in developing miniature pigs
- PMID: 38314265
- PMCID: PMC10837543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24953
Morphogenesis of fungiform papillae in developing miniature pigs
Abstract
Objective: Fungiform papillae contain taste buds and play a critical role in mastication and the gustatory system. In this study, we report a series of sequential observations of organogenesis of fungiform papillae in miniature pigs, as well as changes in the expression of BMP2, BMP4, Wnt5a, Sox2, and Notch1 signaling pathway components.
Design: In this study, we investigated the spatiotemporal expression patterns of BMP, Wnt, Sox2 and Notch in the fungiform papillae of miniature pigs at the bud stage (E40), cap stage (E50) and bell stage (E60). Pregnant miniature pigs were obtained, and the samples were processed for histological staining. Immunohistochemistry and real-time PCR were used to detect the mRNA and protein expression levels of BMP2, BMP4, Wnt5a, Sox2, and Notch1.
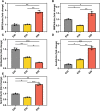
Results: At E40, fungiform papillae were present on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue in a specific array and pattern. The fungiform papillae were enlarged and basically developed at E50 and were largest at the earlier stage (E60). Most of the BMP2 was concentrated in the epithelial layer and the connective tissue core of the fungal papilloma and gradually accumulated from E40-E60. BMP-4 was weakly expressed in the fungiform papillae epithelia, but BMP-4-positive cells were also observed in the developing tongue muscle at E50 and E60. Wnt5a-positive cells were observed in the fungiform papillae epithelia and developing tongue muscle at all three time points. Sox2-positive cells were observed only in fungiform papillae epithelial cells, and Notch1-positive cells could not be detected.
Conclusions: This study provides primary data regarding the morphogenesis and expression of developmental signals in the fungiform papillae of miniature pigs, establishing a foundation for further research in both this model and humans.
Keywords: Development; Fungiform papilla; Immunohistochemistry; Miniature pig.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Lingxiao Wang reports was provided by Beijing Stomatological Hospital, Capital Medical University. Lingxiao Wang reports a relationship with Beijing Stomatological Hospital, 10.13039/501100019871Capital Medical University that includes: funding grants. Lingxiao Wang has patent pending to Lingxiao Wang. No If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Organ cultures of embryonic rat tongue support tongue and gustatory papilla morphogenesis in vitro without intact sensory ganglia.J Comp Neurol. 1997 Jan 20;377(3):324-40. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19970120)377:3<324::aid-cne2>3.0.co;2-4. J Comp Neurol. 1997. PMID: 8989649
-
Expression of BMP2/4/7 during the odontogenesis of deciduous molars in miniature pig embryos.J Mol Histol. 2018 Oct;49(5):545-553. doi: 10.1007/s10735-018-9792-1. Epub 2018 Aug 11. J Mol Histol. 2018. PMID: 30099666
-
Spacing patterns on tongue surface-gustatory papilla.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(2-3):157-61. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.15272380. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15272380 Review.
-
Differential expression of a BMP4 reporter allele in anterior fungiform versus posterior circumvallate taste buds of mice.BMC Neurosci. 2010 Oct 13;11:129. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-129. BMC Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20942907 Free PMC article.
-
Development of fungiform papillae: patterned lingual gustatory organs.Arch Histol Cytol. 2006 Dec;69(4):199-208. doi: 10.1679/aohc.69.199. Arch Histol Cytol. 2006. PMID: 17287575 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

