Potential of lignocellulosic fiber reinforced polymer composites for automobile parts production: Current knowledge, research needs, and future direction
- PMID: 38314269
- PMCID: PMC10837508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24683
Potential of lignocellulosic fiber reinforced polymer composites for automobile parts production: Current knowledge, research needs, and future direction
Abstract
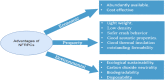
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in research focusing on the use of natural fiber-reinforced polymer composites (NFRPCs) in the automobile industry. These materials offer several advantages over their synthetic counterparts, including lightweight properties, renewability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental friendliness. This increasing research interest in NFRPCs within the automotive sector is primarily aimed at overcoming the challenges that have thus far limited their industrial applications when compared to conventional synthetic composites. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the potential applications and sustainability of lignocellulosic-based NFRPCs in the automobile industry. It examines the current state of knowledge, identifies research needs and existing limitations, and provides insights into future perspectives. This review shows that, while lignocellulosic fibers hold great promise as sustainable, high-performance, and cost-effective alternatives to traditional reinforcing fibers, continuous research is needed to further address issues such as fiber-matrix compatibility, processing techniques, long-term durability concerns, and general property improvement. These advancements are essential to meet the increasing performance demand for eco-friendly, renewable, and energy-efficient materials in automotive design.
Keywords: Automobile parts; Biocomposite; Current knowledge; Lignocellulosic fiber; Polymer matrix.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- AbdurRahman M., Haque S., Athikesavan M.M., Kamaludeen M.B. A review of environmentally friendly green composites: production methods, current progresses, and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Control Ser. 2023;30:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Bhargava P., Gupta N., Kumar R., Vats S. Plant-Microbe Symbiosis. Springer; 2020. Plants and microbes: bioresources for sustainable development and biocontrol; pp. 153–176.
-
- Situmorang Y.A., Zhao Z., Yoshida A., Abudula A., Guan G. Small-scale biomass gasification systems for power generation (< 200 kW class): a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020;117
-
- Liu Y., Li G., Chen Z., Shen Y., Zhang H., Wang S., Gao J. Comprehensive analysis of environmental impacts and energy consumption of biomass-to-methanol and coal-to-methanol via life cycle assessment. Energy. 2020;204
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

