Metronomic chemotherapy and drug repurposing: A paradigm shift in oncology
- PMID: 38314272
- PMCID: PMC10837507
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24670
Metronomic chemotherapy and drug repurposing: A paradigm shift in oncology
Abstract
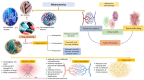
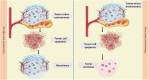
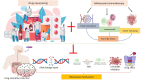
Cancer represents a significant global health and economic burden due to its high mortality rates. While effective in some instances, traditional chemotherapy often falls short of entirely eradicating various types of cancer. It can cause severe side effects due to harm to healthy cells. Two therapeutic approaches have risen to the forefront to address these limitations: metronomic chemotherapy (MCT) and drug repurposing. Metronomic chemotherapy is an innovative approach that breaks from traditional models. It involves the administration of chemotherapeutic regimens at lower doses, without long drug-free intervals that have previously been a hallmark of such treatments. This method offers a significant reduction in side effects and improved disease management. Simultaneously, drug repurposing has gained considerable attraction in cancer treatment. This approach involves utilizing existing drugs, initially developed for other therapeutic purposes, as potential cancer treatments. The application of known drugs in a new context accelerates the timeline from laboratory to patient due to pre-existing safety and dosage data. The intersection of these two strategies gives rise to a novel therapeutic approach named 'Metronomics.' This approach encapsulates the benefits of both MCT and drug repurposing, leading to reduced toxicity, potential for oral administration, improved patient quality of life, accelerated clinical implementation, and enhanced affordability. Numerous clinical studies have endorsed the efficacy of metronomic chemotherapy with tolerable side effects, underlining the potential of Metronomics in better cancer management, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. This review underscores the benefits and applications of metronomic chemotherapy and drug repurposing, specifically in the context of breast cancer, showcasing the promising results of pre-clinical and clinical studies. However, we acknowledge the necessity of additional clinical investigations to definitively establish the role of metronomic chemotherapy in conjunction with other treatments in comprehensive cancer management.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Breast cancer; Conventional chemotherapy; Drug repurposing; Drug resistance; Metronomic chemotherapy.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Zugazagoitia J., et al. Current challenges in cancer treatment. Clin. Therapeut. 2016;38(7):1551–1566. - PubMed
-
- Malani P.N. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. JAMA. 2012;308(17):1813–1814.
-
- Bray F., et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Qayoom H, Mehraj U, Sofi S, Aisha S, Almilaibary A, Alkhanani M, Mir MA. Expression patterns and therapeutic implications of CDK4 across multiple carcinomas: a molecular docking and MD simulation study. Medical Oncology. 2022;39(10):158. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

