3-N-butylphthalide attenuates neuroinflammation in rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease models via the cGAS-STING pathway
- PMID: 38315064
- PMCID: PMC10846052
- DOI: 10.1177/03946320241229041
3-N-butylphthalide attenuates neuroinflammation in rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease models via the cGAS-STING pathway
Abstract
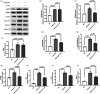
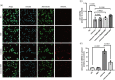
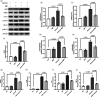
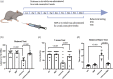
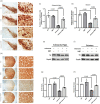
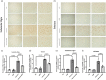
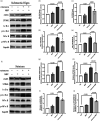
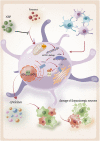
Neuroinflammation is crucial in the onset and progression of dopaminergic neuron loss in Parkinson's disease (PD). We aimed to determine whether 3-N-Butylphthalide (NBP) can protect against PD by inhibiting the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway and the inflammatory response of microglia. MitoSOX/MitoTracker/Hoechst staining was used to detect the levels of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) in BV2 cells. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction was used to measure the levels of free cytoplasmic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in BV2 cells and mouse brain tissues. Behavioral impairments were assessed using rotarod, T-maze, and balance beam tests. Dopaminergic neurons and microglia were observed using immunohistochemical staining. Expression levels of cGAS, STING, nuclear factor kappa-B (NfκB), phospho- NfκB (p-NfκB), inhibitor of NfκBα (IκBα), and phospho-IκBα (p-IκBα) proteins in the substantia nigra and striatum were detected using Western Blot. NBP decreased mitochondrial ROS levels in rotenone-treated BV2 cells. NBP alleviated behavioral impairments and protected against rotenone-induced microgliosis and damage to dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and striatum of rotenone-induced PD mice. NBP decreased rotenone-induced mtDNA leakage and mitigated neuroinflammation by inhibiting cGAS-STING pathway activation. NBP exhibited a protective effect in rotenone-induced PD models by significantly inhibiting the cGAS-STING pathway. Moreover, NBP can alleviate neuroinflammation, and is a potential therapeutic drug for alleviating clinical symptoms and delaying the progression of PD. This study provided insights for the potential role of NBP in PD therapy, potentially mitigating neurodegeneration, and consequently improving the quality of life and lifespan of patients with PD. The limitations are that we have not confirmed the exact mechanism by which NBP decreases mtDNA leakage, and this study was unable to observe the actual clinical therapeutic effect, so further cohort studies are required for validation.
Keywords: 3-N-butylphthalide; Parkinson’s disease; cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes pathway; microglia; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide Rescues Dopaminergic Neurons in Parkinson's Disease Models by Inhibiting the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Ameliorating Mitochondrial Impairment.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 1;12:794770. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.794770. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925379 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between DNA damage and cGAS-STING immune pathway drives neuroinflammation and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease.Brain Behav Immun. 2025 Jul 31:106065. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2025.106065. Online ahead of print. Brain Behav Immun. 2025. PMID: 40752659
-
Type 2 diabetes microenvironment promotes the development of Parkinson's disease by activating microglial cell inflammation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 10;12:1422746. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1422746. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39050892 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA Leakage and cGas/STING Pathway in Microglia: Crosstalk Between Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration.Neuroscience. 2024 Jun 7;548:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.04.009. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Neuroscience. 2024. PMID: 38685462 Review.
-
cGAS-STING and neurodegenerative diseases: A molecular crosstalk and therapeutic perspective.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jun 26;159:114902. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114902. Epub 2025 May 21. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40403503 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitophagy and cGAS-STING crosstalk in neuroinflammation.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Aug;14(8):3327-3361. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.012. Epub 2024 May 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39220869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial DNA leakage: underlying mechanisms and therapeutic implications in neurological disorders.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Feb 7;22(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03363-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 39920753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuroimmune nexus: unraveling the role of the mtDNA-cGAS-STING signal pathway in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Mar 4;20(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00815-2. Mol Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40038765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GDF15 attenuates Parkinson's disease progression via suppressing the activation of cGAS-STING pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jul;480(7):4449-4466. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05265-4. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40178669
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

