Impaired T cells and "memory-like" NK-cell reconstitution is linked to late-onset HCMV reactivation after letermovir cessation
- PMID: 38315873
- PMCID: PMC11302378
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023012008
Impaired T cells and "memory-like" NK-cell reconstitution is linked to late-onset HCMV reactivation after letermovir cessation
Abstract
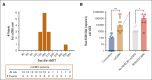
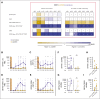
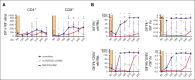
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) is the only cure for many hematologic malignancies. However, alloSCT recipients are susceptible to opportunistic pathogens, such as human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). Letermovir prophylaxis has revolutionized HCMV management, but the challenge of late HCMV reactivations has emerged. Immunological surrogates of clinically significant HCMV infection (csCMVi) after discontinuation of letermovir remain to be defined. Therefore, we studied natural killer (NK)-cell reconstitution along with the global and HCMV pp65-specific T-cell repertoire of 24 alloSCT recipients at 7 time points before (day +90) and after (days +120-270) cessation of letermovir prophylaxis. Patients who experienced csCMVi had lower counts of IFN-γ+ HCMV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells than HCMV controllers. Furthermore, patients with csCMVi displayed late impairment of NK-cell reconstitution, especially suppression of "memory-like" CD159c+CD56dim NK-cell counts that preceded csCMVi events in most patients. Moreover, several surrogates of immune reconstitution were associated with the severity of HCMV manifestation, with patients suffering from HCMV end-organ disease and/or refractory HCMV infection harboring least HCMV-specific T cells and "memory-like" NK cells. Altogether, our findings establish an association of delayed or insufficient proliferation of both HCMV-specific T cells and "memory-like" NK cells with csCMVi and the severity of HCMV manifestations after discontinuation of letermovir prophylaxis.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Immune milestones to predict CMV after letermovir.Blood Adv. 2024 Jun 11;8(11):2964-2966. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024012849. Blood Adv. 2024. PMID: 38861271 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Singh AK, McGuirk JP. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a historical and scientific overview. Cancer Res. 2016;76(22):6445–6451. - PubMed
-
- Broers AE, van Der Holt R, van Esser JW, et al. Increased transplant-related morbidity and mortality in CMV-seropositive patients despite highly effective prevention of CMV disease after allogeneic T-cell-depleted stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2000;95(7):2240–2245. - PubMed
-
- Chemaly RF, Ullmann AJ, Stoelben S, et al. Letermovir for cytomegalovirus prophylaxis in hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(19):1781–1789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

