Machine Learning Predicts Oxaliplatin Benefit in Early Colon Cancer
- PMID: 38315963
- PMCID: PMC11095904
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.01080
Machine Learning Predicts Oxaliplatin Benefit in Early Colon Cancer
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Machine Learning Predicts Oxaliplatin Benefit in Early Colon Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2025 Oct 2:JCO2502281. doi: 10.1200/JCO-25-02281. Online ahead of print. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 41037767 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: A combination of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) is the standard for adjuvant therapy of resected early-stage colon cancer (CC). Oxaliplatin leads to lasting and disabling neurotoxicity. Reserving the regimen for patients who benefit from oxaliplatin would maximize efficacy and minimize unnecessary adverse side effects.
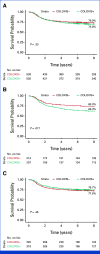
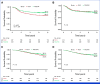
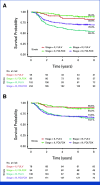
Methods: We trained a new machine learning model, referred to as the colon oxaliplatin signature (COLOXIS) model, for predicting response to oxaliplatin-containing regimens. We examined whether COLOXIS was predictive of oxaliplatin benefits in the CC adjuvant setting among 1,065 patients treated with 5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin (FULV; n = 421) or FULV + oxaliplatin (FOLFOX; n = 644) from NSABP C-07 and C-08 phase III trials. The COLOXIS model dichotomizes patients into COLOXIS+ (oxaliplatin responder) and COLOXIS- (nonresponder) groups. Eight-year recurrence-free survival was used to evaluate oxaliplatin benefits within each of the groups, and the predictive value of the COLOXIS model was assessed using the P value associated with the interaction term (int P) between the model prediction and the treatment effect.
Results: Among 1,065 patients, 526 were predicted as COLOXIS+ and 539 as COLOXIS-. The COLOXIS+ prediction was associated with prognosis for FULV-treated patients (hazard ratio [HR], 1.52 [95% CI, 1.07 to 2.15]; P = .017). The model was predictive of oxaliplatin benefits: COLOXIS+ patients benefited from oxaliplatin (HR, 0.65 [95% CI, 0.48 to 0.89]; P = .0065; int P = .03), but COLOXIS- patients did not (COLOXIS- HR, 1.08 [95% CI, 0.77 to 1.52]; P = .65).
Conclusion: The COLOXIS model is predictive of oxaliplatin benefits in the CC adjuvant setting. The results provide evidence supporting a change in CC adjuvant therapy: reserve oxaliplatin only for COLOXIS+ patients, but further investigation is warranted.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00096278 NCT00004931.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures


References
-
- Schmoll HJ, Van Cutsem E, Stein A, et al. ESMO Consensus Guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal cancer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:2479–2516. - PubMed
-
- Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Macdonald JS, et al. Levamisole and fluorouracil for adjuvant therapy of resected colon carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:352–358. - PubMed
-
- Kuebler JP, Wieand HS, O'Connell MJ, et al. Oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: Results from NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2198–2204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

