Development and psychometric properties evaluation of nurses' innovative behaviours inventory in Iran: protocol for a sequential exploratory mixed-method study
- PMID: 38316597
- PMCID: PMC10860078
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-077056
Development and psychometric properties evaluation of nurses' innovative behaviours inventory in Iran: protocol for a sequential exploratory mixed-method study
Abstract
Introduction: Nurses' innovative behaviours play a crucial role in addressing the challenges including adapting to emerging technologies, resource limitations and social realities such as population ageing that are intricately tied to today's healthcare landscape. Innovative behaviours improve healthcare quality, patient safety and satisfaction. Organisational factors and individual attributes influence nurses' inclination to innovate. With the rise of artificial intelligence and novel technology, healthcare institutions are actively engaged in the pursuit of identifying nurses who demonstrate innovative qualities. Developing a comprehensive protocol to elucidate the various dimensions of nurses' innovative behaviours and constructing a valid measuring instrument, rooted in this protocol represents a significant step in operationalising this concept.
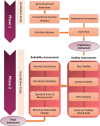
Methods and analysis: The study encompasses two phases: a qualitative study combined with a literature review, followed by the design and psychometric evaluation of the instrument. To ensure diversity, a maximum variation purposive sampling method will be used during the qualitative phase to select clinical nurses. In-depth semistructured interviews will be conducted and analysed using conventional content analysis. Additionally, a comprehensive literature review will supplement any missing features not captured in the qualitative phase, ensuring their inclusion in the primary tool. The subsequent quantitative phase will focus on evaluating the questionnaire's psychometric properties, including face, content and construct validity through exploratory factor analyses (including at least 300 samples) and confirmatory factor analyses (including at least 200 samples). Internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha), reliability (test-retest), responsiveness, interpretability and scoring will also be assessed.
Ethics and dissemination: This study originates from a doctoral dissertation in nursing. Permission and ethical approval from Semnan University of Medical Sciences has been obtained with reference code IR.SEMUMS.1401.226. The study's findings will ultimately be submitted as a research paper to a peer-reviewed journal.
Keywords: Nurses; Nursing Care; Protocols & guidelines; Psychometrics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Yoder-Wise PS, Sportsman S. Leading and Managing in Nursing E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2022.
-
- Afsar B, Cheema S, Bin Saeed B. Do nurses display innovative work behavior when their values match with hospitals’ values EJIM 2018;21:157–71. 10.1108/EJIM-01-2017-0007 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources