Identification and Functional Mechanism Verification of Novel MicroRNAs Associated with the Fibrosis Progression in Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 38316653
- PMCID: PMC11604686
- DOI: 10.1007/s10528-024-10688-7
Identification and Functional Mechanism Verification of Novel MicroRNAs Associated with the Fibrosis Progression in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
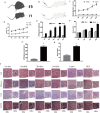
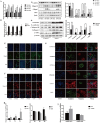
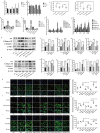
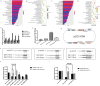
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a serious threat to human health worldwide, and its incidence is increasing annually. A growing amount of information is emerging about the role of micoRNAs (miRNAs) in the regulation of renal fibrosis, which has aroused interest in the development of drugs that block pathogenic miRNAs or restore protective miRNAs levels. To clarify the role of miRNAs in CKD, we selected patients with significant renal fibrotic disease (diabetic nephropathy (DN) and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)) as the disease group, and patients with little or no renal fibrotic disease (minimal change disease (MCD) and renal carcinoma adjacent to normal kidney) as controls. Significantly differentially expressed miRNAs were obtained by human kidney tissue sequencing, subsequently verified in mice models of DN and FSGS, and subsequently inhibited or overexpressed in human renal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2) stimulated by high glucose (HG) and TGF-β1 in vitro. Therefore, the mechanism of its action in renal fibrosis was further elaborated. Finally, the downstream target genes of the corresponding miRNAs were verified by bioinformatics analysis, qRT-PCR, western blot and double luciferase report analysis. Two novel miRNAs, hsa-miR-1470-3p (miR-1470) and hsa-miR-4483-3p (miR-4483), were detected by renal tissue sequencing in the disease group with significant renal fibrosis (DN and FSGS) and the control group with little or no renal fibrosis (MCD and normal renal tissue adjacent to renal carcinoma). Subsequent human renal tissue qRT-PCR verified that the expression of miR-1470 was significantly increased, while the expression of miR-4483 was markedly decreased in the disease group (p < 0.05). Moreover, in vivo DN and FSGS mice models, the expression levels of miR-1470 and miR-4483 were consistent with the results of human kidney tissue. In vitro, miR-4483 was suppressed, whereas miR-1470 was induced by treatment with TGF-β1 or HG. Inhibition of miR-1470 or overexpression of miR-4483 promoted HG or TGF-β1-induced fibrosis in HK-2 cells. Further study revealed that MMP-13 and TIMP1 were the target genes ofmiR-1470 and miR-4483, respectively. Our study identifies newly dysregulated miRNA profiles related to fibrosis kidneys. miR-1470 and miR-4483 are demonstrated to participate in kidney fibrosis by regulation of MMP-13, TIMP1 respectively. Our results may represent a promising research direction for renal disorders and help identify new biomarkers and therapeutic targets for CKD.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; DN; FSGS; Novel miRNAs; Renal fibrosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Ethical Approval: The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board and Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. Every patient had provided written informed consent. All animal experiments were approved by the Committee on Animal Experimentation of Sun Yat-sen University and performed in compliance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the university. Consent for Publication: Not applicable.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intrarenal microRNA signature related to the fibrosis process in chronic kidney disease: identification and functional validation of key miRNAs.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Aug 27;20(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1512-x. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31455266 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-92d-3p suppresses the progression of diabetic nephropathy renal fibrosis by inhibiting the C3/HMGB1/TGF-β1 pathway.Biosci Rep. 2021 Sep 30;41(9):BSR20203131. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203131. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33729484 Free PMC article.
-
Renal microRNA-144-3p is associated with transforming growth factor-β1-induced oxidative stress and fibrosis by suppressing the NRF2 pathway in hypertensive diabetic kidney disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2024 Nov 20;225:546-559. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.10.286. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39423929
-
Roles of microRNAs in renal disorders related to primary podocyte dysfunction.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119463. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119463. Epub 2021 Apr 18. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33862110 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy: From Biomarkers to Therapy.Curr Diab Rep. 2016 Mar;16(3):35. doi: 10.1007/s11892-016-0724-8. Curr Diab Rep. 2016. PMID: 26973290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential biomarkers of recurrent FSGS: a review.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Aug 12;25(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03695-8. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39134955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-106b-5p improving the progression of chronic kidney disease by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad pathway.Hereditas. 2025 Jun 13;162(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00468-7. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40514734 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

