Logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA for genetic tracing of cell identities and state changes
- PMID: 38316783
- PMCID: PMC10844330
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45069-6
Logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA for genetic tracing of cell identities and state changes
Abstract
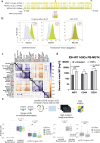
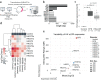
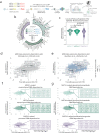
Descriptive data are rapidly expanding in biomedical research. Instead, functional validation methods with sufficient complexity remain underdeveloped. Transcriptional reporters allow experimental characterization and manipulation of developmental and disease cell states, but their design lacks flexibility. Here, we report logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA (LSD), a computational framework leveraging phenotypic biomarkers and trans-regulatory networks as input to design reporters marking the activity of selected cellular states and pathways. LSD uses bulk or single-cell biomarkers and a reference genome or custom cis-regulatory DNA datasets with user-defined boundary regions. By benchmarking validated reporters, we integrate LSD with a computational ranking of phenotypic specificity of putative cis-regulatory DNA. Experimentally, LSD-designed reporters targeting a wide range of cell states are functional without minimal promoters. Applied to broadly expressed genes from human and mouse tissues, LSD generates functional housekeeper-like sLCRs compatible with size constraints of AAV vectors for gene therapy applications. A mesenchymal glioblastoma reporter designed by LSD outperforms previously validated ones and canonical cell surface markers. In genome-scale CRISPRa screens, LSD facilitates the discovery of known and novel bona fide cell-state drivers. Thus, LSD captures core principles of cis-regulation and is broadly applicable to studying complex cell states and mechanisms of transcriptional regulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.G. reports a patent application EP18192715 by the Max-Delbrück-Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC), Robert-Rössle-Str. 10, 13092 Berlin, Germany. No disclosures are to be reported by the other authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Optimization of synthetic molecular reporters for a mesenchymal glioblastoma transcriptional program by integer programing.Bioinformatics. 2022 Sep 2;38(17):4162-4171. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac488. Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35809064
-
Promoter Boundaries for the luxCDABE and betIBA-proXWV Operons in Vibrio harveyi Defined by the Method Rapid Arbitrary PCR Insertion Libraries (RAIL).J Bacteriol. 2018 May 9;200(11):e00724-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00724-17. Print 2018 Jun 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29531178 Free PMC article.
-
A cis-regulatory logic simulator.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Jul 27;8:272. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-272. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17662143 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the molecular basis of tissue-specific gene expression in plants: Can synthetic biology help?Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2022 Aug;68:102241. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102241. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35700675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic Promoters: Designing the cis Regulatory Modules for Controlled Gene Expression.Mol Biotechnol. 2018 Aug;60(8):608-620. doi: 10.1007/s12033-018-0089-0. Mol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29855997 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological modulators of epithelial immunity uncovered by synthetic genetic tracing of SARS-CoV-2 infection responses.Sci Adv. 2023 Jun 23;9(25):eadf4975. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf4975. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37343108 Free PMC article.
-
Oncofetal reprogramming drives phenotypic plasticity in WNT-dependent colorectal cancer.Nat Genet. 2025 Feb;57(2):402-412. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-02058-1. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Nat Genet. 2025. PMID: 39930084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schepers, A. G. et al. Lineage tracing reveals Lgr5+ stem cell activity in mouse intestinal adenomas. Science337, 730–735 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

