Identification of myeloid-derived growth factor as a mechanically-induced, growth-promoting angiocrine signal for human hepatocytes
- PMID: 38316785
- PMCID: PMC10844291
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44760-y
Identification of myeloid-derived growth factor as a mechanically-induced, growth-promoting angiocrine signal for human hepatocytes
Abstract
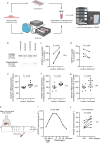
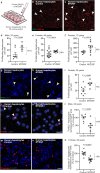
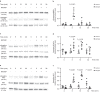
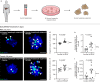
Recently, we have shown that after partial hepatectomy (PHx), an increased hepatic blood flow initiates liver growth in mice by vasodilation and mechanically-triggered release of angiocrine signals. Here, we use mass spectrometry to identify a mechanically-induced angiocrine signal in human hepatic endothelial cells, that is, myeloid-derived growth factor (MYDGF). We show that it induces proliferation and promotes survival of primary human hepatocytes derived from different donors in two-dimensional cell culture, via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). MYDGF also enhances proliferation of human hepatocytes in three-dimensional organoids. In vivo, genetic deletion of MYDGF decreases hepatocyte proliferation in the regenerating mouse liver after PHx; conversely, adeno-associated viral delivery of MYDGF increases hepatocyte proliferation and MAPK signaling after PHx. We conclude that MYDGF represents a mechanically-induced angiocrine signal and that it triggers growth of, and provides protection to, primary mouse and human hepatocytes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood flow-induced angiocrine signals promote organ growth and regeneration.Bioessays. 2025 Feb;47(2):e2400207. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400207. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39529434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) facilitates hepatocyte proliferation and liver regeneration in mice.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1992-2003. doi: 10.1002/hep.26235. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23299899 Free PMC article.
-
Inductive angiocrine signals from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration.Nature. 2010 Nov 11;468(7321):310-5. doi: 10.1038/nature09493. Nature. 2010. PMID: 21068842 Free PMC article.
-
Role of vasodilation in liver regeneration and health.Biol Chem. 2021 Apr 27;402(9):1009-1019. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2021-0155. Print 2021 Aug 26. Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33908220 Review.
-
Endothelial Notch activation reshapes the angiocrine of sinusoidal endothelia to aggravate liver fibrosis and blunt regeneration in mice.Hepatology. 2018 Aug;68(2):677-690. doi: 10.1002/hep.29834. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Hepatology. 2018. PMID: 29420858 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Myeloid-derived growth factor in diseases: structure, function and mechanisms.Mol Med. 2024 Jul 19;30(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00874-z. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39030488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood flow-induced angiocrine signals promote organ growth and regeneration.Bioessays. 2025 Feb;47(2):e2400207. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400207. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39529434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaphorin-3A regulates liver sinusoidal endothelial cell porosity and promotes hepatic steatosis.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Jun;3(6):734-753. doi: 10.1038/s44161-024-00487-z. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 39196233 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

