The siRNA-mediated knockdown of AP-1 restores the function of the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle by reducing perivascular and interstitial fibrosis and key molecular players in cardiopulmonary disease
- PMID: 38317144
- PMCID: PMC10845748
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-04933-1
The siRNA-mediated knockdown of AP-1 restores the function of the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle by reducing perivascular and interstitial fibrosis and key molecular players in cardiopulmonary disease
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a complex multifactorial vascular pathology characterized by an increased pulmonary arterial pressure, vasoconstriction, remodelling of the pulmonary vasculature, thrombosis in situ and inflammation associated with right-side heart failure. Herein, we explored the potential beneficial effects of treatment with siRNA AP-1 on pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), right ventricular dysfunction along with perivascular and interstitial fibrosis in pulmonary artery-PA, right ventricle-RV and lung in an experimental animal model of monocrotaline (MCT)-induced PAH.
Methods: Golden Syrian hamsters were divided into: (1) C group-healthy animals taken as control; (2) MCT group obtained by a single subcutaneous injection of 60 mg/kg MCT at the beginning of the experiment; (3) MCT-siRNA AP-1 group received a one-time subcutaneous dose of MCT and subcutaneous injections containing 100 nM siRNA AP-1, every two weeks. All animal groups received water and standard chow ad libitum for 12 weeks.
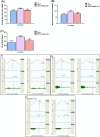
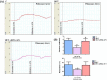
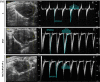
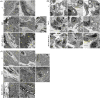
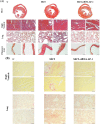
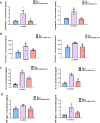
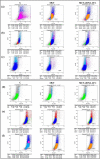
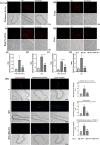
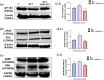
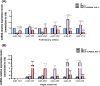
Results: In comparison with the MCT group, siRNA AP-1 treatment had significant beneficial effects on investigated tissues contributing to: (1) a reduction in TGF-β1/ET-1/IL-1β/TNF-α plasma concentrations; (2) a reduced level of cytosolic ROS production in PA, RV and lung and notable improvements regarding the ultrastructure of these tissues; a decrease of inflammatory and fibrotic marker expressions in PA (COL1A/Fibronectin/Vimentin/α-SMA/CTGF/Calponin/MMP-9), RV and lung (COL1A/CTGF/Fibronectin/α-SMA/F-actin/OB-cadherin) and an increase of endothelial marker expressions (CD31/VE-cadherin) in PA; (4) structural and functional recoveries of the PA [reduced Vel, restored vascular reactivity (NA contraction, ACh relaxation)] and RV (enlarged internal cavity diameter in diastole, increased TAPSE and PRVOFs) associated with a decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate; (5) a reduced protein expression profile of AP-1S3/ pFAK/FAK/pERK/ERK and a significant decrease in the expression levels of miRNA-145, miRNA-210, miRNA-21, and miRNA-214 along with an increase of miRNA-124 and miRNA-204.
Conclusions: The siRNA AP-1-based therapy led to an improvement of pulmonary arterial and right ventricular function accompanied by a regression of perivascular and interstitial fibrosis in PA, RV and lung and a down-regulation of key inflammatory and fibrotic markers in MCT-treated hamsters.
Keywords: Cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis; Cardiopulmonary disease; Monocrotaline; Pulmonary arterial hypertension; siRNA AP-1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Pulmonary arterial hypertension induced by a novel method: Twice-intraperitoneal injection of monocrotaline.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Aug;243(12):995-1003. doi: 10.1177/1535370218794128. Epub 2018 Aug 12. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 30099957 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of eIF3a alleviates pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition via TGFβ1/SMAD pathway.J Transl Med. 2025 May 9;23(1):524. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06505-3. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40346622 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Metabolic Reprogramming of Right Ventricular Fibroblasts in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase-Dependent Shift in Mitochondrial Metabolism Promotes Right Ventricular Fibrosis.Circ Res. 2020 Jun 5;126(12):1723-1745. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316443. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32216531 Free PMC article.
-
Diastolic dysfunction in pulmonary artery hypertension: Creatine kinase and the potential therapeutic benefit of beta-blockers.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2018 Apr;45(4):384-389. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12898. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29193283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Monocrotaline Rat Model of Right Heart Disease Induced by Pulmonary Artery Hypertension.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 23;12(9):1944. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12091944. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335458 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wolter J, Mooi KG. Histopathology of pulmonary hypertensive diseases. Diagn Histopathol. 2006;12:429–440. doi: 10.1016/j.cdip.2006.07.003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

