Preliminary nomogram model for predicting irreversible organ damage of patients with systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 38317497
- PMCID: PMC11781586
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae083
Preliminary nomogram model for predicting irreversible organ damage of patients with systemic sclerosis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate predictive factors for irreversible organ damage in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and establish a nomogram model.
Methods: This retrospective study included patients with SSc who were treated at our hospital between March 2013 and March 2023. Irreversible organ damage included heart failure, respiratory failure, renal failure, and gangrene of the hands and feet. Cox and LASSO regression analyses were performed to determine the predictive factors. Based on the results, a nomogram model was developed. The model was evaluated using the C-indices, calibration plots and DCA.
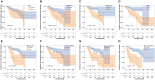
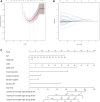
Results: A total of 361 patients with systemic sclerosis were randomly divided into the development (n = 181) and validation (n = 180) groups. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that age ≥65 years, weight loss, digital ulcers, mRSS ≥16, elevated creatinine, elevated myoglobin, elevated C-reactive protein, renal involvement and cardiac involvement were independent risk factors. Based on the LASSO analysis, a nomogram model of irreversible organ damage was established. The C-indices of the development group at 24, 60 and 96 m were 96.7, 84.5 and 85.7, whereas those of the validation group at 24, 60 and 96 m were 86.6, 79.1 and 78.5, respectively. The results of the DCA showed that the nomogram can be used as a valuable tool to predict irreversible organ damage in patients with SSc.
Conclusion: We included commonly used clinical indicators. According to the nomogram, the probability of irreversible organ damage can be calculated and high-risk patients can be identified.
Keywords: biomarker; cardiovascular; gastrointestinal; hormone; observational study; renal; skin.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Risk factor analysis on body mass rebound after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and establishment of a nomogram prediction model].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Oct 25;25(10):913-920. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20220418-00159. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36245117 Chinese.
-
A nomogram for predicting the risk of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Int J Cardiol. 2024 Jul 15;407:131973. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2024.131973. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Int J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38508321
-
A preliminary probabilistic nomogram model for predicting renal arteriolar damage in IgA nephropathy from clinical parameters.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 1;15:1435838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1435838. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39011045 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram for predicting 28-day mortality in elderly patients with acute kidney injury receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: a secondary analysis based on a retrospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Jun 11;25(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03628-5. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38862887 Free PMC article.
-
[Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting 3-month mortality risk in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 May;36(5):465-470. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231218-01091. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38845491 Chinese.
References
-
- The Lancet. Systemic sclerosis: advances and prospects. Lancet 2017;390:1624. - PubMed
-
- Campochiaro C, Allanore Y, Braun-Moscovici Y, Matucci-Cerinic M, Balbir-Gurman A. Is cyclophosphamide still the gold standard in early severe rapidly progressive systemic sclerosis? Autoimmun Rev 2023;103439. - PubMed
-
- Lescoat A, Kato H, Varga J. Emerging cellular and immunotherapies for systemic sclerosis: from mesenchymal stromal cells to CAR-T cells and vaccine-based approaches. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2023;35:356–63. - PubMed
-
- Thoreau B, Chaigne B, Renaud A, Mouthon L. Treatment of systemic sclerosis. Presse Med 2021;50:104088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

