Robust anti-tumor T cell response with efficient intratumoral infiltration by nanodisc cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 38317797
- PMCID: PMC10843840
- DOI: 10.1002/adtp.202000094
Robust anti-tumor T cell response with efficient intratumoral infiltration by nanodisc cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
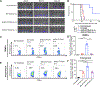
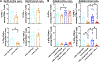
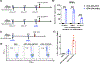
Potent anti-tumor T cell response and efficient intratumoral T cell infiltration are the major challenges for therapeutic cancer vaccines. To address these issues, a nano-vaccine system has been designed to promote anti-tumor T cell responses, and intratumoral infiltration was examined in various murine tumor models. Subcutaneous vaccination with nanodiscs carrying human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 E7 antigen elicits as high as ~32% E7-specific CD8 α + T cell responses in circulation, representing a 29-fold improvement over the soluble peptide vaccination. Importantly, nanodisc vaccination also promotes robust intratumoral T cell infiltration and eliminates HPV16 E6/E7-expressing TC-1 tumors at mucosal sites, including lungs, inner lip, and intravaginal tissues. In a benchmark study with a live Listeria vaccine combined with anti-PD-1 IgG, nanodiscs plus anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade elicits comparable levels of T cell responses with anti-tumor efficacy. Furthermore, compared with Complete Freund's Adjuvant combined with tetanus toxoid, nanodisc vaccination in HLA-A02 mice generates >200-fold stronger IFN-γ+ T cell responses against a neoantigen from an HLA-A02 melanoma patient. Overall, these results show that the nanodisc system is a promising cancer vaccine platform for inducing anti-tumor T cell responses.
Keywords: cancer vaccine; nanoparticles; neoantigen; papillomavirus.
Conflict of interest statement
A patent application for nanodisc vaccines has been filed, with J.J.M., A.S., and R.K. as inventors. J.J.M. and A.S. are co-founders of EVOQ Therapeutics, LLC. that develops the nanodisc technology for vaccine applications. P.B.S. and R.J. are employees of Bristol Myers Squibb. C.J.W. is a co-founder, equity holder, and SAB member of Neon Therapeutics, Inc. D.B.K. has previously advised Neon Therapeutics, and has received consulting fees from Gerson Lehrman Group, Guidepoint, Neon Therapeutics, System analytic Ltd and The Science Advisory Board. D.B.K. owns equity in Aduro Biotech, Agenus Inc., Armata Pharmaceuticals, Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc., Breakbio Corp., Bristol Myers Squibb Co., Celldex Therapeutics Inc., Editas Medicine Inc., Exelixis Inc., Gilead Sciences Inc., IMV Inc., Lexicon Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Stemline Therapeutics Inc.
Figures
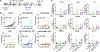
Similar articles
-
PD-1 blockade synergizes with intratumoral vaccination of a therapeutic HPV protein vaccine and elicits regression of tumor in a preclinical model.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Apr;70(4):1049-1062. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02754-x. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33108473 Free PMC article.
-
Development of DNA Vaccine Targeting E6 and E7 Proteins of Human Papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) and HPV18 for Immunotherapy in Combination with Recombinant Vaccinia Boost and PD-1 Antibody.mBio. 2021 Jan 19;12(1):e03224-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03224-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33468698 Free PMC article.
-
A Therapeutic DNA Vaccine Targeting HPV16 E7 in Combination with Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Enhanced Tumor Regression and Cytotoxic Immune Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15469. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015469. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895145 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose-Modified Liposome Co-Delivery of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E7 Peptide and CpG Oligodeoxynucleotide Adjuvant Enhances Antitumor Activity Against Established Large TC-1 Grafted Tumors in Mice.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Dec 1;15:9571-9586. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S275670. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33293808 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination with a nanoparticle E7 vaccine can prevent tumor recurrence following surgery in a human papillomavirus head and neck cancer model.Oncoimmunology. 2021 Apr 13;10(1):1912473. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1912473. Oncoimmunology. 2021. PMID: 33907631 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Engineered Nanoparticles for Cancer Vaccination and Immunotherapy.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Oct 20;53(10):2094-2105. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00456. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 33017150 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-bio interfaces effect of two-dimensional nanomaterials and their applications in cancer immunotherapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Nov;11(11):3447-3464. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.004. Epub 2021 May 16. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34900529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using Mesoporous Silica-Based Dual Biomimetic Nano-Erythrocytes for an Improved Antitumor Effect.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 15;15(12):2785. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122785. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140125 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine nanodiscs plus polyICLC elicit robust CD8+ T cell responses in mice and non-human primates.J Control Release. 2021 Sep 10;337:168-178. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.07.026. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 34280415 Free PMC article.
-
Current Landscape of Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2926:1-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4542-0_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40266513 Review.
References
-
- Sahin U, Tureci O, Science. 2018, 359, 1355. - PubMed
-
- Romero P, Banchereau J, Bhardwaj N, Cockett M, Disis ML, Dranoff G, Gilboa E, Hammond SA, Hershberg R, Korman AJ, Kvistborg P, Melief C, Mellman I, Palucka AK, Redchenko I, Robins H, Sallusto F, Schenkelberg T, Schoenberger S, Sosman J, Tureci O, Van den Eynde B, Koff W, Coukos G, Sci Transl Med. 2016, 8, 334ps9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- R01 NS122536/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007767/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB022563/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE031951/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA271799/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155010/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA210273/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE026728/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS091555/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA279391/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125087/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201300006C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA101942/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA216772/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE030691/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
