Clinico-Radiological Correlation of Weber's Syndrome
- PMID: 38318538
- PMCID: PMC10839420
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.51624
Clinico-Radiological Correlation of Weber's Syndrome
Abstract
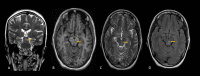
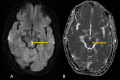
Weber's syndrome, named after Hermann Weber, is characterized by midbrain lesions often caused by strokes, resulting in ipsilateral third nerve palsy, including ptosis and pupillary abnormalities, and contralateral hemiplegia. We discuss a case of a 35-year-old lady with cognitive impairment, right hemiparesis, diplopia, left eye ptosis, and lateral eye deviation. MRI of the brain with contrast suggested an acute infarct in the left-sided paramedian region of the midbrain. The oculomotor nucleus and cerebral peduncle were both affected by an abrupt left-sided paramedian midbrain stroke. The participation of particular midbrain nuclei together with symptoms including drooping eyelids, diplopia, and limb paralysis suggested Weber's syndrome. An MRI study of the brain is the modality of choice in suspected stroke cases and is more sensitive when it comes to the brainstem lesions. A comprehensive neurological examination with a clinical diagnosis of Weber's syndrome before radiological investigations is of great help for localizing brain stem lesions and thus aids in early diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: brain stem stroke; mri brain; oculomotor nucleus; paramedian mid brain infarct; weber’s syndrome.
Copyright © 2024, Hatgaonkar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- The crossed paralyses. The original brain-stem syndromes of Millard-Gubler, Foville, Weber, and Raymond-Cestan. Silverman IE, Liu GT, Volpe NJ, Galetta SL. Arch Neurol. 1995;52:635–638. - PubMed
-
- Weber syndrome - clinical-imaging correlations. Lupescu IC, Anghel D, Dulamea AO. Ro J Neurol. 2022;21:247–250.
-
- A patient with reversible pupil-sparing Weber’s syndrome. Umasankar U, Huwez FU. https://www.neurologyindia.com/text.asp?2003/51/3/388/1181. Neurol India. 2003;51:388–389. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
