Glycerol-derived organic carbonates: environmentally friendly plasticizers for PLA
- PMID: 38318613
- PMCID: PMC10840682
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra08922c
Glycerol-derived organic carbonates: environmentally friendly plasticizers for PLA
Abstract
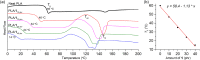
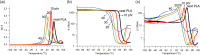
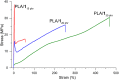
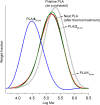
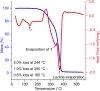
Polylactic acid (PLA) stands as a promising material, sourced from renewables and exhibiting biodegradability-albeit under stringent industrial composting settings. A primary challenge impeding PLA's broad applications is its inherent brittleness, as it fractures with minimal elongation despite its commendable tensile strength. A well-established remedy involves blending PLA with plasticizers. In this study, a range of organic carbonates-namely, 4-ethoxycarbonyloximethyl-[1,3]dioxolan-2-one (1), 4-methoxycarbonyloximethyl-[1,3]dioxolan-2-one (2), glycerol carbonate (3), and glycerol 1-acetate 2,3-carbonate (4)-were synthesized on a preparative scale (∼100 g), using renewable glycerol and CO2-derived diethyl carbonate (DEC) or dimethyl carbonate (DMC). Significantly, 1-4 exhibited biodegradability under ambient conditions within a week, ascertained through soil exposure at 25 °C-outpacing the degradation of comparative cellulose. Further investigations revealed 1's efficacy as a PLA plasticizer. Compatibility with PLA, up to 30 phr (parts per hundred resin), was verified using an array of techniques, including DSC, DMA, SEM, and rotational rheometry. The resulting blends showcased enhanced ductility, evident from tensile property measurements. Notably, the novel plasticizer 1 displayed an advantage over conventional acetyltributylcitrate (ATBC) in terms of morphological stability. Slow crystallization, observed in PLA/ATBC blends over time at room temperature, was absent in PLA/1 blends, preserving amorphous domain dimensions and mitigating plasticizer migration-confirmed through DMA assessments of aged and unaged specimens. Nevertheless, biodegradation assessments of the blends revealed that the biodegradable organic carbonate plasticizers did not augment PLA's biodegradation. The PLA in the blends remained mostly unchanged under ambient soil conditions of 25 °C over a 6 month period. This work underscores the potential of organic carbonates as both eco-friendly plasticizers for PLA and as biodegradable compounds, contributing to the development of environmentally conscious polymer systems.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Heyn R. H., Chapter 7 – Organic carbonates, in Carbon Dioxide Utilisation, ed. Styring P., Quadrelli E. A. and Armstrong K., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2015, pp. 97–113
-
- Schäffner B. Schäffner F. Verevkin S. P. Börner A. Organic Carbonates as Solvents in Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010;110(8):4554–4581. - PubMed
-
- Porcar R. Lozano P. Burguete M. I. Garcia-Verdugo E. Luis S. V. Dimethyl carbonate as a non-innocent benign solvent for the multistep continuous flow synthesis of amino alcohols. React. Chem. Eng. 2018;3(4):572–578.
-
- Michan A. L. Parimalam B. S. Leskes M. Kerber R. N. Yoon T. Grey C. P. Lucht B. L. Fluoroethylene Carbonate and Vinylene Carbonate Reduction: Understanding Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolyte Additives and Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation. Chem. Mater. 2016;28(22):8149–8159.
-
- Szőri M. Giri B. R. Wang Z. Dawood A. E. Viskolcz B. Farooq A. Glycerol carbonate as a fuel additive for a sustainable future. Sustainable Energy Fuels. 2018;2(10):2171–2178.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

