Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR in ophiocordyceps sinensis under different experimental conditions
- PMID: 38319940
- PMCID: PMC10846742
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287882
Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR in ophiocordyceps sinensis under different experimental conditions
Abstract
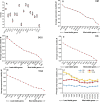
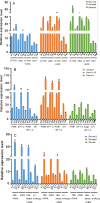
The Chinese caterpillar mushroom, Ophiocordyceps sinensis (O. sinensis), is a rarely medicinal fungus in traditional chinese herbal medicine due to its unique medicinal values, and the expression stability of reference genes is essential to normalize its gene expression analysis. In this study, BestKeeper, NormFinder and geNorm, three authoritative statistical arithmetics, were applied to evaluate the expression stability of sixteen candidate reference genes (CRGs) in O. sinensis under different stress [low temperature (4°C), light treatment (300 lx), NaCl (3.8%)] and different development stages (mycelia, primordia and fruit bodies) and formation of morphologic mycelium (aeriasubstrate, hyphae knot mycelium). The paired variation values indicated that two genes could be enough to accurate standardization exposed to different conditions of O.sinensis. Among these sixteen CRGs, 18S ribosomal RNA (18S rRNA) and beta-Tubulin (β-TUB) showed the topmost expression stability in O.sinensis exposed to all conditions, while glutathione hydrolase proenzym (GGT) and Phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI) showed the least expression stability. The optimal reference gene in different conditions was various. β-TUB and Ubiquitin (UBQ) were identified as the two most stable genes in different primordia developmental stage, while phosphoglucomutase (PGM) with elongation factor 1-alpha (EF1-α) and 18S rRNA with UBQ were the most stably expressed for differentially morphologic mycelium stages and different stresses, respectively. These results will contribute to more accurate evaluation of the gene relative expression levels in O.sinensis under different conditions using the optimal reference gene in real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis.
Copyright: © 2024 He et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

