A genetic association study of circulating coagulation factor VIII and von Willebrand factor levels
- PMID: 38320121
- PMCID: PMC11443575
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2023021452
A genetic association study of circulating coagulation factor VIII and von Willebrand factor levels
Abstract
Coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) and its carrier protein von Willebrand factor (VWF) are critical to coagulation and platelet aggregation. We leveraged whole-genome sequence data from the Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine (TOPMed) program along with TOPMed-based imputation of genotypes in additional samples to identify genetic associations with circulating FVIII and VWF levels in a single-variant meta-analysis, including up to 45 289 participants. Gene-based aggregate tests were implemented in TOPMed. We identified 3 candidate causal genes and tested their functional effect on FVIII release from human liver endothelial cells (HLECs) and VWF release from human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mendelian randomization was also performed to provide evidence for causal associations of FVIII and VWF with thrombotic outcomes. We identified associations (P < 5 × 10-9) at 7 new loci for FVIII (ST3GAL4, CLEC4M, B3GNT2, ASGR1, F12, KNG1, and TREM1/NCR2) and 1 for VWF (B3GNT2). VWF, ABO, and STAB2 were associated with FVIII and VWF in gene-based analyses. Multiphenotype analysis of FVIII and VWF identified another 3 new loci, including PDIA3. Silencing of B3GNT2 and the previously reported CD36 gene decreased release of FVIII by HLECs, whereas silencing of B3GNT2, CD36, and PDIA3 decreased release of VWF by HVECs. Mendelian randomization supports causal association of higher FVIII and VWF with increased risk of thrombotic outcomes. Seven new loci were identified for FVIII and 1 for VWF, with evidence supporting causal associations of FVIII and VWF with thrombotic outcomes. B3GNT2, CD36, and PDIA3 modulate the release of FVIII and/or VWF in vitro.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.J.L. received funding in 2020 from Novartis for a research grant. B.M.P. serves on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. L.M.R. is a consultant for the TOPMed Administrative Coordinating Center through WeStat. R.L.-G. is a part-time consultant for Metabolon, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Complete lists of the members of TOPMed and INVENT appear in the supplemental Appendix.
Figures

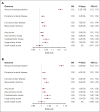
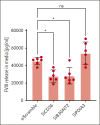
Comment in
-
Novel risk loci for thrombotic factors.Blood. 2024 May 2;143(18):1790-1792. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024023891. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38696197 No abstract available.
References
-
- Swami A, Kaur V. A concise review and update for the practicing physician. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2017;23(8):900–910. - PubMed
-
- Chavin SI. Factor VIII: structure and function in blood clotting. Am J Hematol. 1984;16(3):297–306. - PubMed
-
- Terraube V, O'Donnell JS, Jenkins PV. Factor VIII and von Willebrand factor interaction: biological, clinical and therapeutic importance. Haemophilia. 2010;16(1):3–13. - PubMed
-
- Lippi G, Franchini M, Salvagno GL, Montagnana M, Poli G, Guidi GC. Correlation between von Willebrand factor antigen, von Willebrand factor ristocetin cofactor activity and factor VIII activity in plasma. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2008;26(2):150–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_UU_00007/10/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131136/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139553/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL172780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 HL141791/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002490/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134894/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

