Controlling Adsorption of Diblock Copolymer Nanoparticles onto an Aldehyde-Functionalized Hydrophilic Polymer Brush via pH Modulation
- PMID: 38320303
- PMCID: PMC10883040
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c03392
Controlling Adsorption of Diblock Copolymer Nanoparticles onto an Aldehyde-Functionalized Hydrophilic Polymer Brush via pH Modulation
Abstract
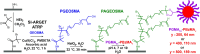
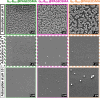
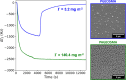
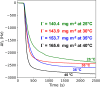
Sterically stabilized diblock copolymer nanoparticles with a well-defined spherical morphology and tunable diameter were prepared by RAFT aqueous emulsion polymerization of benzyl methacrylate at 70 °C. The steric stabilizer precursor used for these syntheses contained pendent cis-diol groups, which means that such nanoparticles can react with a suitable aldehyde-functional surface via acetal bond formation. This principle is examined herein by growing an aldehyde-functionalized polymer brush from a planar silicon wafer and studying the extent of nanoparticle adsorption onto this model substrate from aqueous solution at 25 °C using a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM). The adsorbed amount, Γ, depends on both the nanoparticle diameter and the solution pH, with minimal adsorption observed at pH 7 or 10 and substantial adsorption achieved at pH 4. Variable-temperature QCM studies provide strong evidence for chemical adsorption, while scanning electron microscopy images recorded for the nanoparticle-coated brush surface after drying indicate mean surface coverages of up to 62%. This fundamental study extends our understanding of the chemical adsorption of nanoparticles on soft substrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Covalent Capture of Nanoparticle-Stabilized Oil Droplets via Acetal Chemistry Using a Hydrophilic Polymer Brush.Langmuir. 2024 Dec 17;40(50):26735-26741. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c03897. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 39641918 Free PMC article.
-
Capturing Enzyme-Loaded Diblock Copolymer Vesicles Using an Aldehyde-Functionalized Hydrophilic Polymer Brush.Langmuir. 2024 Jul 9;40(27):14086-14098. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c01561. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 38934738 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorption of Aldehyde-Functional Diblock Copolymer Spheres onto Surface-Grafted Polymer Brushes via Dynamic Covalent Chemistry Enables Friction Modification.Chem Mater. 2023 Jul 19;35(15):6109-6122. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c01227. eCollection 2023 Aug 8. Chem Mater. 2023. PMID: 37576584 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine-Functionalized Diblock Copolymer Nanoparticles Exhibit Enhanced Adsorption onto Planar Stainless Steel.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2023 Aug;44(16):e2200903. doi: 10.1002/marc.202200903. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2023. PMID: 36534428 Free PMC article.
-
Mucoadhesive pickering nanoemulsions via dynamic covalent chemistry.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023 Dec;651:334-345. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.07.162. Epub 2023 Jul 27. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023. PMID: 37544222
Cited by
-
Covalent Capture of Nanoparticle-Stabilized Oil Droplets via Acetal Chemistry Using a Hydrophilic Polymer Brush.Langmuir. 2024 Dec 17;40(50):26735-26741. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c03897. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 39641918 Free PMC article.
-
Dipolar Brush Polymers: A Numerical Study of the Force Exerted onto a Penetrating Colloidal Particle Under an External Field.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jan 29;17(3):366. doi: 10.3390/polym17030366. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39940567 Free PMC article.
-
Capturing Enzyme-Loaded Diblock Copolymer Vesicles Using an Aldehyde-Functionalized Hydrophilic Polymer Brush.Langmuir. 2024 Jul 9;40(27):14086-14098. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c01561. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 38934738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keddie J. L.; Meredith P.; Jones R. A. L.; Donald A. M. Kinetics of film formation in acrylic latices studied with multiple-angle-of-incidence ellipsometry and environmental sem. Macromolecules 1995, 28 (8), 2673–2682. 10.1021/ma00112a012. - DOI
-
- do Amaral M.; Roos A.; Asua J. M.; Creton C. Assessing the effect of latex particle size and distribution on the rheological and adhesive properties of model waterborne acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesives films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 281 (2), 325–338. 10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.142. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Binks B. P. Particles as surfactants—similarities and differences. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7 (1–2), 21–41. 10.1016/S1359-0294(02)00008-0. - DOI

