Trastuzumab deruxtecan in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38320430
- PMCID: PMC10937193
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.102233
Trastuzumab deruxtecan in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) has shown promising results in patients with breast cancer brain metastases (BCBMs). We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of T-DXd in the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive BCBM population.
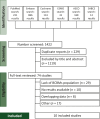
Patients and methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases as well as American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO), and San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) websites for clinical trials (CTs) and observational studies evaluating T-DXd in patients with HER2-positive BCBM. Heterogeneity was assessed with I2 statistics. Random effects models were used for all statistical analyses, which were carried out using R software (version 4.2.2).
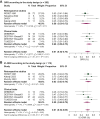
Results: Ten studies were included, six CTs (n = 189) and four observational studies (n = 130), with a total of 319 patients. The median progression-free survival was 15 months [95% confidence interval (CI) 13.9-16.1 months]. The objective response rate (ORR) was 61% (95% CI 52% to 70%), and the intracranial (IC)-ORR was 61% (95% CI 54% to 69%). No significant differences in ORR and IC-ORR were observed between CTs and observational studies (P = 0.31 and 0.58, respectively). The clinical benefit rate (CBR) was 80% (95% CI 52% to 94%), and the IC-CBR was 70% (95% CI 54% to 82%). The ORR was 68% (95% CI 57% to 77%) in the subgroup of patients with stable BMs and 60% (95% CI 48%-72%) in patients with active BM, with no significant difference between groups (P = 0.35).
Conclusions: Our systematic review and meta-analysis supports the IC activity of T-DXd in patients with stable BM and active BM.
Trial registration: International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under the protocol number CRD42023422589.
Keywords: HER+; T-DXd; antibody-drug conjugate; brain metastases; breast cancer; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; trastuzumab deruxtecan.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

