Recurrent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in a Saudi Girl
- PMID: 38322079
- PMCID: PMC10846910
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.51813
Recurrent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in a Saudi Girl
Abstract
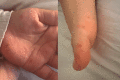
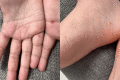
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a viral illness that predominantly affects infants and children, causing blisters and sores on the hands, feet, and mouth. Recurrence is rare, but a case in a six-year-old girl in Saudi Arabia was reported. A six-year-old girl presented with a rash on her palms and soles, which was preceded by a mild sore throat and low-grade fever. She had been in contact with her two-year-old sister, who had similar symptoms but a different rash pattern. During clinical examination, multiple erythematous deep-seated vesicles and papules were noted on the patient's palms and soles, with no involvement of mucous membranes or nails. The diagnosis of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) was made based on the characteristic clinical presentation, and the rash resolved within seven days without treatment or complications. The patient had experienced a similar presentation six months ago, which was also diagnosed as HFMD, and the rash had resolved spontaneously within one week. In her second episode, the rash was less severe, with milder prodromal symptoms. In both episodes, the lesions were asymptomatic and had no mucosal involvement. The patient had experienced onychomadesis after her first episode, but no nail abnormalities were seen after her second episode. Although HFMD is rare to recur in children, outbreaks can lead to another episode. HFMD prevalence is underestimated in Saudi Arabia due to missed mild cases. Pediatricians and dermatologists should be aware of HFMD incidence and its complications, as early detection is vital in preventing outbreaks and transmission.
Keywords: children; hand-foot-mouth disease; pediatric dermatology; rash; recurrence; saudi arabia; viral illness.
Copyright © 2024, Alakrash et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Onychomadesis and Beau's Line Following Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease in a Seven-Year-Old Male.Cureus. 2022 Apr 4;14(4):e23832. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23832. eCollection 2022 Apr. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35530819 Free PMC article.
-
[Hand, foot and mouth disease--more than a harmless "childhood disease"].Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2014 Jan;37(1):4-10; quiz 11-2. Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24490433 Review. German.
-
Notes from the field: severe hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with coxsackievirus A6 - Alabama, Connecticut, California, and Nevada, November 2011-February 2012.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012 Mar 30;61(12):213-4. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012. PMID: 22456122
-
Dermatological spectrum of hand, foot and mouth disease from classical to generalized exanthema.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Apr;33(4):e92-8. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000120. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014. PMID: 24463804
-
Onychomadesis after hand-foot-and-mouth disease outbreak in northern Greece: case series and brief review of the literature.Int J Dermatol. 2015 Sep;54(9):1039-44. doi: 10.1111/ijd.12592. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Int J Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25772385 Review.
Cited by
-
Current trends and challenges in the management of foot and mouth disease in Saudi Arabia: A review.Open Vet J. 2025 May;15(5):1907-1933. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i5.6. Epub 2025 May 31. Open Vet J. 2025. PMID: 40557100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guerra AM, Orille E, Waseem M. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease. - PubMed
-
- Enterovirus A71 containing codon-deoptimized VP1 and high-fidelity polymerase as next-generation vaccine candidate. Tsai YH, Huang SW, Hsieh WS, Cheng CK, Chang CF, Wang YF, Wang JR. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02308-18 J Virol. 2019;93 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreak by Coxsackievirus A6 during COVID-19 pandemic in 2021, São Paulo, Brazil. Carmona RCC, Machado BC, Reis FC, et al. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105245. J Clin Virol. 2022;154:105245–105210. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hand-foot-mouth disease in an adult. Gomes S, Santos S, Ferreira Maia I, Verissimo R, Carvalho T. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105245 Cureus. 2023;15:0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- The history of Enterovirus A71 outbreaks and molecular epidemiology in the Asia-Pacific region. Puenpa J, Wanlapakorn N, Vongpunsawad S, Poovorawan Y. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-019-0573-2. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26:75. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources