The hemiclamshell approach to bulky cervico-mediastinal lesions: how to do it
- PMID: 38322192
- PMCID: PMC10839522
- DOI: 10.21037/med-23-36
The hemiclamshell approach to bulky cervico-mediastinal lesions: how to do it
Abstract
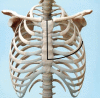
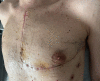
The hemiclamshell incision is a combination of partial median sternotomy and anterolateral thoracotomy, allowing excellent exposure of mediastinum, one pleural cavity and the neck. It can be used for superior sulcus tumors with mediastinal involvement or to resect bulky mediastinal lesions or lesions requiring cervical, mediastinal and pleural exposition. Although the vast majority of mediastinal lesions can now be approached by minimally invasive techniques, the hemiclamshell incision still plays a pivotal role in the case of bulky lesions involving cervical, mediastinal and pleural cavities. In the case of cardiac or great vessel involvement, the procedure should be performed in experienced high-volume centers with the availability of cardio-pulmonary bypass, extra-corporeal membrane oxygenator or venous shunts. Although the vast majority of mediastinal lesions can now be approached by minimally invasive techniques, the hemiclamshell incision still plays a pivotal role in the case of bulky lesions involving cervical, mediastinal and pleural cavities. It consists of a combination of subtotal median vertical sternotomy and antero-lateral thoracotomy in the 4th intercostal space, providing excellent exposure of the neck, mediastinum and one pleural cavity. The objective of this paper is to describe the standard steps for performing a hemiclamshell incision by using modern devices and technology which contribute to make this procedure easier, faster and safer.
Keywords: Hemiclamshell; mediastinum; sternotomy; thoracotomy; thymoma.
2024 Mediastinum. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://med.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/med-23-36/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
