Ganoderic acid A attenuated hepatic impairment by down-regulating the intracellular JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway in induced mushroom poisoning
- PMID: 38322557
- PMCID: PMC10839386
- DOI: 10.62347/ERWA6712
Ganoderic acid A attenuated hepatic impairment by down-regulating the intracellular JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway in induced mushroom poisoning
Abstract
Background: Mushroom poisoning is one of the most prominent public health problems. However, there is no special antidote so far. In the present study, we verified that Ganoderma lucidum may be an effective approach for treatment of acute mushroom poisoning.
Methods: A retrospective study was performed within the past 20 years, we compiled information on the treatment of α-Amatoxin mushroom poisoning with Ganoderma lucidum by evaluating the mortality rate and liver function before and after treatment. Moreover, we explore the potential underlying mechanism of Ganoderma lucidum in the treatment of α-amanita poisoning in both in vivo animal experiments and in vitro cell experiments.
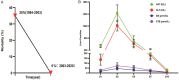
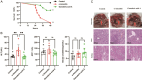
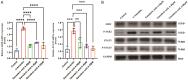
Results: In our study, a total of 556 cases of mushroom poisoning were integrated over the past 20 years, the primary outcome was in-hospital mortality. Specificity, descriptive data of ALT, AST, BA and STB were evaluated for the effectiveness of protection to acute liver damage. From 1994 to 2002, there were 55 cases of mushroom poisoning in which 372 individuals were poisoned, 129 individuals died, with a mortality of 35%. Since 2002, after being treated with Ganoderma lucidum, surprisingly, the mortality decreased to 0%, and all the 184 patients were cured, the hepatic impairment improved significantly within 10 days. Based on a multivariate logistic regression analyses, after adjusting for age, gender and baseline clinical indicators, it was found that Ganoderma lucidum treatment was effective in reducing the morbidity (OR = 0.58), and Ganoderma lucidum treatment also showed an improvement in liver enzymes and in shortening the length of hospitalization significantly. Meanwhile, the main components of Ganoderma lucidum, Ganoderic acid A could significantly improve the survival rate and liver function in α-Amatoxin poisoned mice and may effectively inhibit the JAK2-STAT3 pathway, which could contribute to the detoxification in poisoned patients.
Conclusion: Ganoderma lucidum is very effective in treating mushroom poisoning by α-amanita and is worth promoting.
Keywords: Ganoderma lucidum; Ganoderma lucidum A; liver toxicity; mushroom poisoning; α-amatoxin.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Potential Activity of Lingzhi or Reishi Medicinal Mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum (Agaricomycetes), to Alleviate Liver Injury in Adults with Acute Mushroom Poisoning: A Retrospective Study.Int J Med Mushrooms. 2022;24(5):57-72. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2022043524. Int J Med Mushrooms. 2022. PMID: 35695589
-
Clinical experience in treatment of Amanita mushroom poisoning with Glossy Ganoderma Decoction and routine Western medicines.Chin J Integr Med. 2007 Jun;13(2):145-7. doi: 10.1007/s11655-007-0145-2. Chin J Integr Med. 2007. PMID: 17609916
-
Suppression of Cisplatin-Induced Hepatic Injury in Rats Through Alarmin High-Mobility Group Box-1 Pathway by Ganoderma lucidum: Theoretical and Experimental Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Jun 11;14:2335-2353. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S249093. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32606602 Free PMC article.
-
Amatoxin-Containing Mushroom Poisonings: Species, Toxidromes, Treatments, and Outcomes.Wilderness Environ Med. 2018 Mar;29(1):111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.wem.2017.10.002. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Wilderness Environ Med. 2018. PMID: 29325729 Review.
-
Germplasm resources and secondary metabolism regulation in Reishi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum).Chin Herb Med. 2023 Jun 10;15(3):376-382. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2023.01.005. eCollection 2023 Jul. Chin Herb Med. 2023. PMID: 37538858 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on the Biological Activity of Ganoderic Acids in Ganoderma lucidum over the Last Five Years.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 21;14(10):1339. doi: 10.3390/life14101339. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mas A. Mushrooms, amatoxins and the liver. J Hepatol. 2005;42:166–169. - PubMed
-
- Stone R. Toxicology. Heart-stopping revelation about how Chinese mushroom kills. Science. 2012;335:1293. - PubMed
-
- Treatment of mushroom poisoning. JAMA. 1985;253:3252. - PubMed
-
- Fiume L, Sperti S, Montanaro L, Busi C, Costantino D. Amanitins do not bind to serum albumin. Lancet. 1977;1:1111. - PubMed
-
- Xiao GL, Liu FY, Chen ZH. Clinical observation on treatment of Russula subnigricans poisoning patients by Ganoderma lucidum decoction. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2003;23:278–280. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
