Music combined with dexmedetomidine relieves preoperative anxiety and promotes postoperative recovery in patients undergoing gynecologic laparoscopic surgery: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 38322568
- PMCID: PMC10839387
- DOI: 10.62347/DSMC5610
Music combined with dexmedetomidine relieves preoperative anxiety and promotes postoperative recovery in patients undergoing gynecologic laparoscopic surgery: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effects of music combined with dexmedetomidine on perioperative anxiety and postoperative recovery in gynecologic laparoscopic patients.
Methods: A total of 82 female patients were enrolled in this study. Patients were randomized to the patient-preferred Music+Dexmedetomidine group (M+DEX group, n=41) and the Dexmedetomidine group (DEX group, n=41). Prior to the induction of anesthesia, dexmedetomidine was pumped intravenously at 0.5 µg/kg for 10 minutes in both groups and then maintained at 0.2 µg/kg/hour until 30 minutes before the end of surgery. In contrast to the patients in the DEX group, the patients in the M+DEX group listened to 5 minutes of their favorite music during dexmedetomidine infusion. The primary outcome was the patient's preoperative State Anxiety Inventory (SAI) score. The secondary outcomes included visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores and QoR-15 scores at 24 hours postoperatively.
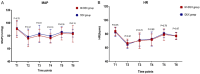
Results: The clinical data of a total of 82 patients were analyzed. After the music intervention, we found that the preoperative SAI scores were lower in the M+DEX group than in the DEX group (37.9±5.6 vs. 41.5±6.9; P=0.01). The M+DEX group had lower VAS scores at 24 hours postoperatively than the DEX group (1 (1.0, 2.0) vs. 2 (2.0, 3.0), P < 0.01), and the M+DEX group had higher QoR-15 scores at 24 hours after the surgery than the DEX group (127.7±10.0 vs. 122.3±11.2; P=0.03).
Conclusion: Patients undergoing gynecologic laparoscopic surgery who listened to their favorite music before the induction of anesthesia had less preoperative anxiety and recovered better 24 hours postoperatively than those who only received dexmedetomidine.
Keywords: Music; anxiety; dexmedetomidine; gynecological laparoscopic surgery; postoperative recovery.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Ultrasound-Guided Deep Serratus Anterior Plane Block Combined With Dexmedetomidine as an Adjuvant to Ropivacaine Inpatient Quality of Recovery Scores Undergoing Modified Radical Mastectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 31;12:858030. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.858030. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35433468 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of erector spinae plane block with different doses of dexmedetomidine as adjuvant for ropivacaine on the postoperative quality of recovery after video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy surgery: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Aug 7;23(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02231-9. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37550610 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Dexmedetomidine Alone for Intravenous Patient-Controlled Analgesia After Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery: A Consort-Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 May;95(19):e3639. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003639. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27175680 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of intravenous lidocaine, dexmedetomidine and their combination on postoperative pain and bowel function recovery after abdominal hysterectomy.Minerva Anestesiol. 2017 Jul;83(7):685-694. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.16.11472-5. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Minerva Anestesiol. 2017. PMID: 28094477 Clinical Trial.
-
Analgesic Effects of Ropivacaine Combined With Dexmedetomidine in Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Perianesth Nurs. 2023 Jun;38(3):493-503. doi: 10.1016/j.jopan.2022.09.003. Epub 2023 Jan 27. J Perianesth Nurs. 2023. PMID: 36710235
Cited by
-
Latent profiles and determinants of postoperative sleep quality in elective surgery patients.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 3;15(1):617. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84896-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39753664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li XR, Zhang WH, Williams JP, Li T, Yuan JH, Du Y, Liu JD, Wu Z, Xiao ZY, Zhang R, Liu GK, Zheng GR, Zhang DY, Ma H, Guo QL, An JX. A multicenter survey of perioperative anxiety in China: pre- and postoperative associations. J Psychosom Res. 2021;147:110528. - PubMed
-
- Carr E, Brockbank K, Allen S, Strike P. Patterns and frequency of anxiety in women undergoing gynaecological surgery. J Clin Nurs. 2006;15:341–352. - PubMed
-
- Sobol-Kwapinska M, Babel P, Plotek W, Stelcer B. Psychological correlates of acute postsurgical pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pain. 2016;20:1573–1586. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
