Construction of a Multi-Indicator Model for Abscess Prediction in Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis Using Inflammatory Indicators
- PMID: 38323114
- PMCID: PMC10844011
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S443765
Construction of a Multi-Indicator Model for Abscess Prediction in Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis Using Inflammatory Indicators
Abstract
Background: Granulomatous lobular mastitis (GLM) is a chronic inflammatory breast disease, and abscess formation is a common complication of GLM. The process of abscess formation is accompanied by changes in multiple inflammatory markers. The present study aimed to construct a diagnosis model for the early of GLM abscess formation based on multiple inflammatory parameters.
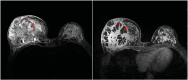
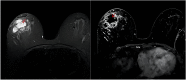
Methods: Based on the presence or absence of abscess formation on breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), 126 patients with GLM were categorised into an abscess group (85 patients) and a non-abscess group (41 patients). Demographic characteristics and the related laboratory results for the 9 inflammatory markers were collected. Logistics univariate analysis and collinearity test were used for selecting independent variables. A regression model to predict abscess formation was constructed using Logistics multivariate analysis.
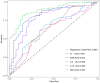
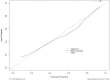
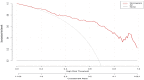
Results: The univariate and multivariate analysis showed that the N, ESR, IL-4, IL-10 and INF-α were independent diagnostic factors of abscess formation in GLM (P<0. 05). The nomogram was drawn on the basis of the logistics regression model. The area under the curve (AUC) of the model was 0.890, which was significantly better than that of a single indicator and the sensitivity and specificity of the model were high (81.2% and 85.40%, respectively). These results predicted by the model were highly consistent with the actual diagnostic results. The results of this calibration curve indicated that the model had a good value and stability in predicting abscess formation in GLM. The decision curve analysis (DCA) demonstrated a satisfactory positive net benefit of the model.
Conclusion: A predictive model for abscess formation in GLM based on inflammatory markers was constructed in our study, which may provide a new strategy for early diagnosis and treatment of the abscess stage of GLM.
Keywords: ROC curve; abscess formation; diagnostic model; granulomatous lobular mastitis; inflammation; risk factors.
© 2024 Du et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of a machine learning-based diagnostic model using hematological parameters to differentiate periductal mastitis from granulomatous lobular mastitis.Sci Prog. 2025 Apr-Jun;108(2):368504251333513. doi: 10.1177/00368504251333513. Epub 2025 Apr 13. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40223288 Free PMC article.
-
Discrimination Model Construction for Non-Lactational Mastitis and Breast Cancer Based on Imaging Features.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2024 Oct 30;85(10):1-15. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2024.0278. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39475019
-
A new stage for predicting the prognosis of granulomatous lobular mastitis.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 19;20(3):e0319956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319956. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40106498 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological manifestations of granulomatous lobular mastitis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 2;11:1326587. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1326587. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38371511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of granulomatous lobular mastitis: an international multidisciplinary consensus (2021 edition).Mil Med Res. 2022 Apr 26;9(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40779-022-00380-5. Mil Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35473758 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic determinants of inflammatory cytokines and their causal relationship with inflammatory disorders of breast: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 1;15(1):7300. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91723-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40025158 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

