Linezolid brain penetration in neurointensive care patients
- PMID: 38323369
- PMCID: PMC10904716
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkae025
Linezolid brain penetration in neurointensive care patients
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Linezolid brain penetration in neurointensive care patients.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025 Jun 3;80(6):1751. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaf099. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40105881 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Linezolid exposure in critically ill patients is associated with high inter-individual variability, potentially resulting in subtherapeutic antibiotic exposure. Linezolid exhibits good penetration into the CSF, but its penetration into cerebral interstitial fluid (ISF) is unknown.
Objectives: To determine linezolid penetration into CSF and cerebral ISF of neurointensive care patients.
Patients and methods: Five neurocritical care patients received 600 mg of linezolid IV twice daily for treatment of extracerebral infections. At steady state, blood and CSF samples were collected from arterial and ventricular catheters, and microdialysate was obtained from a cerebral intraparenchymal probe.
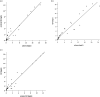
Results: The median fAUC0-24 was 57.6 (24.9-365) mg·h/L in plasma, 64.1 (43.5-306.1) mg·h/L in CSF, and 27.0 (10.7-217.6) mg·h/L in cerebral ISF. The median penetration ratio (fAUCbrain_or_CSF/fAUCplasma) was 0.5 (0.25-0.81) for cerebral ISF and 0.92 (0.79-1) for CSF. Cerebral ISF concentrations correlated well with plasma (R = 0.93, P < 0.001) and CSF levels (R = 0.93, P < 0.001).The median fAUC0-24/MIC ratio was ≥100 in plasma and CSF for MICs of ≤0.5 mg/L, and in cerebral ISF for MICs of ≤0.25 mg/L. The median fT>MIC was ≥80% of the dosing interval in CSF for MICs of ≤0.5 mg/L, and in plasma and cerebral ISF for MICs of ≤0.25 mg/L.
Conclusions: Linezolid demonstrates a high degree of cerebral penetration, and brain concentrations correlate well with plasma and CSF levels. However, substantial variability in plasma levels, and thus cerebral concentrations, may result in subtherapeutic tissue concentrations in critically ill patients with standard dosing, necessitating therapeutic drug monitoring.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures