Real-world Experience of Abrocitinib Treatment in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis and Hand Eczema: Up to 28-week Results from the BioDay Registry
- PMID: 38323500
- PMCID: PMC10863496
- DOI: 10.2340/actadv.v104.19454
Real-world Experience of Abrocitinib Treatment in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis and Hand Eczema: Up to 28-week Results from the BioDay Registry
Abstract
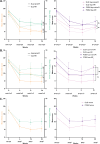
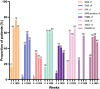
Limited daily practice data on the effect of abrocitinib in patients with atopic dermatitis are available. The aim of this multicentre prospective study is to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of abrocitinib in patients with atopic dermatitis treated in daily practice. In a subgroup, the effectiveness of abrocitinib on hand eczema was evaluated. A total of 103 patients from the BioDay registry were included in the study: week 4 (n = 95), week 16 (n = 61) and week 28 (n = 39). At week 28, the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI)-50/75/90 was achieved by 81.8%, 57.6%, and 18.2%, respectively, and the weekly average pruritus numerical rating scale ≤ 4 by 62.9%. The effectiveness of abrocitinib was not significantly different between dupilumab non-responders and dupilumab-naïve patients/responders, and between upadacitinib non-responders and upadacitinib-naïve patients/responders. Mean ± standard deviation Hand Eczema Severity Index decreased from 27.4 ± 27.7 at baseline to 7.7 ± 12.1 at week 28 (n = 31). Thirty-two patients (31.1%) discontinued treatment due to ineffectiveness (n = 17), adverse events (n = 9) or both (n = 3). The most frequently reported adverse event was nausea (n = 28). In conclusion, abrocitinib is an effective treatment for atopic dermatitis and can be effective for patients with previous inadequate response to dupilumab or upadacitinib. Furthermore, hand eczema can improve in patients treated with abrocitinib for atopic dermatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
CMB Boesjes is a speaker for AbbVie and Eli Lilly. IH is a consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi. Klaziena Politiek received consultancy fees for AbbVie, LEO Pharma and Sanofi Genzyme. LFvdG is a speaker for AbbVie, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi. MdG is a consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker for AbbVie Almirall, Eli Lilly, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi. MSdB-W is a consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker for AbbVie, Almirall, Aslan, Arena, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. MLAS is a consultant, advisory board member and/or speaker for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galderma, LEO Pharma, Pfizer, and Sanofi. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Werfel T, Allam JP, Biedermann T, Eyerich K, Gilles S, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. . Cellular and molecular immunologic mechanisms in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016; 138: 336–349. - PubMed
-
- Simpson EL, Thompson MM, Hanifin JM. Prevalence and morphology of hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis 2006; 17: 123–127. - PubMed
-
- Thyssen JP, Schuttelaar MLA, Alfonso JH, Andersen KE, Angelova-Fischer I, Arents BWM, et al. . Guidelines for diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis 2022; 86: 357–378. - PubMed
-
- Mikhaylov D, Ungar B, Renert-Yuval Y, Guttman-Yassky E. Oral Janus kinase inhibitors for atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2023; 130: 577–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

