Negative emotions mediate the association between the topology of the complex brain network and smartphone use disorder: A resting-state EEG study
- PMID: 38324061
- PMCID: PMC10988397
- DOI: 10.1556/2006.2023.00077
Negative emotions mediate the association between the topology of the complex brain network and smartphone use disorder: A resting-state EEG study
Abstract
Background: Increasing research has examined the factors related to smartphone use disorder. However, limited research has explored its neural basis.
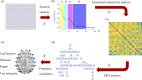
Aims: We aimed to examine the relationship between the topology of the resting-state electroencephalography (rs-EEG) brain network and smartphone use disorder using minimum spanning tree analysis. Furthermore, we examined how negative emotions mediate this relationship.
Methods: This study included 113 young, healthy adults (mean age = 20.87 years, 46.9% males).
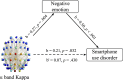
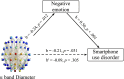
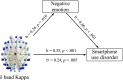
Results: The results showed that the alpha- and delta-band kappas and delta-band leaf fraction were positively correlated with smartphone use disorder. In contrast, the alpha-band diameter was negatively correlated with smartphone use disorder. Negative emotions fully mediated the relationship between alpha-band kappa and alpha-band diameter and smartphone use disorder. Furthermore, negative emotions partially mediated the relationship between delta-band kappa and smartphone use disorder. The findings suggest that excessive scale-free alpha- and delta-band brain networks contribute to the emergence of smartphone use disorder. In addition, the findings also demonstrate that negative emotions and smartphone use disorder share the same neural basis. Negative emotions play a mediating role in the association between topological deviations and smartphone use disorder.
Discussion: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to examine the neural basis of smartphone use disorder from the perspective of the topology of the rs-EEG brain network. Therefore, neuromodulation may be a potential intervention for smartphone use disorder.
Keywords: minimum spanning tree; negative emotions; resting-state EEG; smartphone use disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abnormal functional connectivity of EEG gamma band in patients with depression during emotional face processing.Clin Neurophysiol. 2015 Nov;126(11):2078-89. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.12.026. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25766267
-
Loss of EEG Network Efficiency Is Related to Cognitive Impairment in Dementia With Lewy Bodies.Mov Disord. 2015 Nov;30(13):1785-93. doi: 10.1002/mds.26309. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Mov Disord. 2015. PMID: 26179663
-
Resting-state EEG reveals global network deficiency in dyslexic children.Neuropsychologia. 2020 Feb 17;138:107343. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2020.107343. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Neuropsychologia. 2020. PMID: 31952981
-
Opportunities and methodological challenges in EEG and MEG resting state functional brain network research.Clin Neurophysiol. 2015 Aug;126(8):1468-81. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.11.018. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25511636 Review.
-
Mapping cognitive and emotional networks in neurosurgical patients using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging.Neurosurg Focus. 2020 Feb 1;48(2):E9. doi: 10.3171/2019.11.FOCUS19773. Neurosurg Focus. 2020. PMID: 32006946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Babiloni, C., Lopez, S., Noce, G., Ferri, R., Panerai, S., Catania, V., … Carducci, F. (2023). Relationship between default mode network and resting-state electroencephalographic alpha rhythms in cognitively unimpaired seniors and patients with dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. Cerebral Cortex, 33(20), 10514–10527. 10.1093/cercor/bhad300. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bian, M., & Leung, L. (2014). Linking loneliness, shyness, smartphone addiction symptoms, and patterns of smartphone use to social capital. Social Science Computer Review, 33(1), 61–79. 10.1177/0894439314528779. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

