CD23+IgG1+ memory B cells are poised to switch to pathogenic IgE production in food allergy
- PMID: 38324641
- PMCID: PMC11008013
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adi0673
CD23+IgG1+ memory B cells are poised to switch to pathogenic IgE production in food allergy
Abstract
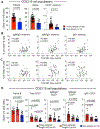
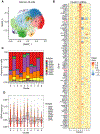
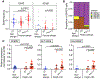
Food allergy is caused by allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies, but little is known about the B cell memory of persistent IgE responses. Here, we describe, in human pediatric peanut allergy, a population of CD23+IgG1+ memory B cells arising in type 2 immune responses that contain high-affinity peanut-specific clones and generate IgE-producing cells upon activation. The frequency of CD23+IgG1+ memory B cells correlated with circulating concentrations of IgE in children with peanut allergy. A corresponding population of "type 2-marked" IgG1+ memory B cells was identified in single-cell RNA sequencing experiments. These cells differentially expressed interleukin-4 (IL-4)- and IL-13-regulated genes, such as FCER2/CD23+, IL4R, and germline IGHE, and carried highly mutated B cell receptors (BCRs). In children with high concentrations of serum peanut-specific IgE, high-affinity B cells that bind the main peanut allergen Ara h 2 mapped to the population of "type 2-marked" IgG1+ memory B cells and included clones with convergent BCRs across different individuals. Our findings indicate that CD23+IgG1+ memory B cells transcribing germline IGHE are a unique memory population containing precursors of high-affinity pathogenic IgE-producing cells that are likely to be involved in the long-term persistence of peanut allergy.
Figures
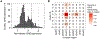

Update of
-
The memory of pathogenic IgE is contained within CD23 + IgG1 + memory B cells poised to switch to IgE in food allergy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 25:2023.01.25.525506. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.25.525506. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Sci Transl Med. 2024 Feb 7;16(733):eadi0673. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adi0673. PMID: 36747707 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Sicherer SH, Sampson HA, Food allergy: A review and update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141, 41–58 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Berkowska MA, Heeringa JJ, Hajdarbegovic E, van der Burg M, Thio HB, van Hagen PM, Boon L, Orfao A, van Dongen JJ, van Zelm MC, Human IgE(+) B cells are derived from T cell-dependent and T cell-independent pathways. J Allergy Clin Immunol 134, 688–697 e686 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Heeringa JJ, Rijvers L, Arends NJ, Driessen GJ, Pasmans SG, van Dongen JJM, de Jongste JC, van Zelm MC, IgE-expressing memory B cells and plasmablasts are increased in blood of children with asthma, food allergy, and atopic dermatitis. Allergy, (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

