Rac1 promotes kidney collecting duct repair by mechanically coupling cell morphology to mitotic entry
- PMID: 38324689
- PMCID: PMC10849615
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi7840
Rac1 promotes kidney collecting duct repair by mechanically coupling cell morphology to mitotic entry
Abstract
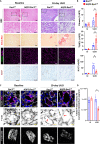
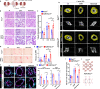
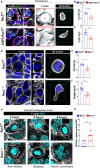
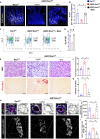
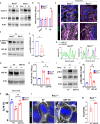
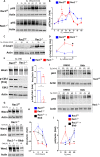
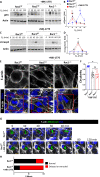
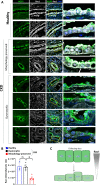
Prolonged obstruction of the ureter, which leads to injury of the kidney collecting ducts, results in permanent structural damage, while early reversal allows for repair. Cell structure is defined by the actin cytoskeleton, which is dynamically organized by small Rho guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases). In this study, we identified the Rho GTPase, Rac1, as a driver of postobstructive kidney collecting duct repair. After the relief of ureteric obstruction, Rac1 promoted actin cytoskeletal reconstitution, which was required to maintain normal mitotic morphology allowing for successful cell division. Mechanistically, Rac1 restricted excessive actomyosin activity that stabilized the negative mitotic entry kinase Wee1. This mechanism ensured mechanical G2-M checkpoint stability and prevented premature mitotic entry. The repair defects following injury could be rescued by direct myosin inhibition. Thus, Rac1-dependent control of the actin cytoskeleton integrates with the cell cycle to mediate kidney tubular repair by preventing dysmorphic cells from entering cell division.
Figures



References
-
- Forbes M. S., Thornhill B. A., Minor J. J., Gordon K. A., Galarreta C. I., Chevalier R. L., Fight-or-flight: Murine unilateral ureteral obstruction causes extensive proximal tubular degeneration, collecting duct dilatation, and minimal fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 303, F120–F129 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hiatt M. J., Ivanova L., Trnka P., Solomon M., Matsell D. G., Urinary tract obstruction in the mouse: The kinetics of distal nephron injury. Lab. Invest. 93, 1012–1023 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK069921/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD033412/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002025/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- K08 DK134879/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127589/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL154287/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056942/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX005240/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- I01 BX002196/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK135931/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL163195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK114809/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

