Oxygen Targets in Neonatal Pulmonary Hypertension: Individualized, "Precision-Medicine" Approach
- PMID: 38325948
- PMCID: PMC10857735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clp.2023.12.003
Oxygen Targets in Neonatal Pulmonary Hypertension: Individualized, "Precision-Medicine" Approach
Abstract
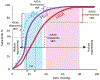
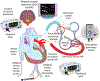
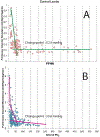
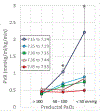
Oxygen is a specific pulmonary vasodilator. Hypoxemia causes pulmonary vasoconstriction, and normoxia leads to pulmonary vasodilation. However, hyperoxia does not enhance pulmonary vasodilation but causes oxidative stress. There are no clinical trials evaluating optimal oxygen saturation or Pao2 in pulmonary hypertension. Data from translational studies and case series suggest that oxygen saturation of 90% to 97% or Pao2 between 50 and 80 mm Hg is associated with the lowest pulmonary vascular resistance.
Keywords: Alveolar oxygen; Oxygen saturation; Pulmonary vascular resistance; Superoxide anions.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Moudgil R, Michelakis ED, Archer SL. Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Journal of applied physiology. 2005;98(1):390–403. - PubMed
-
- Steurer MA, Jelliffe-Pawlowski LL, Baer RJ, Partridge JC, Rogers EE, Keller RL. Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn in Late Preterm and Term Infants in California. Pediatrics. 2017;139(1). - PubMed

