Tractable Quinolone Hydrazides Exhibiting Sub-Micromolar and Broad Spectrum Antitrypanosomal Activities
- PMID: 38326914
- PMCID: PMC11076157
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202300667
Tractable Quinolone Hydrazides Exhibiting Sub-Micromolar and Broad Spectrum Antitrypanosomal Activities
Abstract
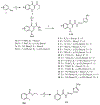
Nagana and Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT), caused by (sub)species of Trypanosoma, are diseases that impede human and animal health, and economic growth in Africa. The few drugs available have drawbacks including suboptimal efficacy, adverse effects, drug resistance, and difficult routes of administration. New drugs are needed. A series of 20 novel quinolone compounds with affordable synthetic routes was made and evaluated in vitro against Trypanosoma brucei and HEK293 cells. Of the 20 compounds, 12 had sub-micromolar potencies against the parasite (EC50 values=0.051-0.57 μM), and most were non-toxic to HEK293 cells (CC50 values>5 μM). Two of the most potent compounds presented sub-micromolar activities against other trypanosome (sub)species (T. cruzi and T. b. rhodesiense). Although aqueous solubility is poor, both compounds possess good logD values (2-3), and either robust or poor microsomal stability profiles. These varying attributes will be addressed in future reports.
Keywords: Drug; Hydrazide; Nagana; Quinolone; Trypanosomiasis.
© 2024 The Authors. ChemMedChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests
The authors affirm that they have no known financial or interpersonal conflicts that would have appeared to have an impact on the research presented in this study.
Figures

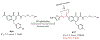

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

