Incidence and outcomes of kidney replacement therapy for end-stage kidney disease due to primary glomerular disease in Europe: findings from the ERA Registry
- PMID: 38327216
- PMCID: PMC11483622
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfae034
Incidence and outcomes of kidney replacement therapy for end-stage kidney disease due to primary glomerular disease in Europe: findings from the ERA Registry
Abstract
Background: Primary glomerular disease (PGD) is a major cause of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) leading to kidney replacement therapy (KRT). We aimed to describe incidence (trends) in individuals starting KRT for ESKD due to PGD and to examine their survival and causes of death.
Methods: We used data from the European Renal Association (ERA) Registry on 69 854 patients who started KRT for ESKD due to PGD between 2000 and 2019. ERA primary renal disease codes were used to define six PGD subgroups. We examined age and sex standardized incidence, trend of the incidence and survival.
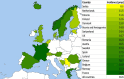
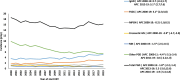
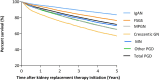
Results: The standardized incidence of KRT for ESKD due to PGD was 16.6 per million population (pmp), ranging from 8.6 pmp in Serbia to 20.0 pmp in France. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) had the highest incidences, of 4.6 pmp and 2.6 pmp, respectively. Histologically non-examined PGDs represented over 50% of cases in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Romania and were also common in Greece, Estonia, Belgium and Sweden. The incidence declined from 18.6 pmp in 2000 to 14.5 pmp in 2013, after which it stabilized. All PGD subgroups had 5-year survival probabilities above 50%, with crescentic glomerulonephritis having the highest risk of death [adjusted hazard ratio 1.8 (95% confidence interval 1.6-1.9)] compared with IgAN. Cardiovascular disease was the most common cause of death (33.9%).
Conclusion: The incidence of KRT for ESKD due to PGD showed large differences between countries and was highest and increasing for IgAN and FSGS. Lack of kidney biopsy facilities in some countries may have affected accurate assignment of the cause of ESKD. The recognition of the incidence and outcomes of KRT among different PGD subgroups may contribute to a more individualized patient care approach.
Keywords: dialysis; epidemiology; kidney replacement therapy; outcome; primary glomerular disease.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Canadian Institute for Health Information. Treatment of end-stage organ failure in Canada, Canadian Organ Replacement Register, 2011 to2020: end-stage kidney disease and kidney transplants—Data tables. https://view.officeapps.live.com/op/view.aspx?src=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cihi...
-
- United States Renal Data System . 2022 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2022.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

