Range extensions of Pacific bone-eating worms (Annelida, Siboglinidae, Osedax)
- PMID: 38327359
- PMCID: PMC10848615
- DOI: 10.3897/BDJ.11.e102803
Range extensions of Pacific bone-eating worms (Annelida, Siboglinidae, Osedax)
Abstract
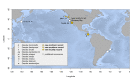
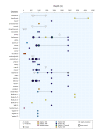
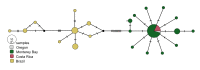
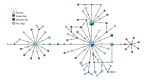
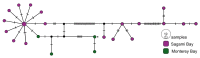
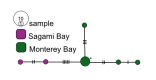
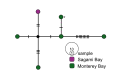
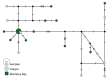
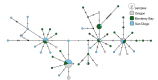
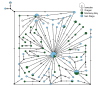
First described in 2004 off California, Osedax worms are now known from many of the world's oceans, ranging from 10 to over 4000 m in depth. Currently, little is known about species ranges, since most descriptions are from single localities. In this study, we used new sampling in the north-eastern Pacific and available GenBank data from off Japan and Brazil to report expanded ranges for five species: Osedaxfrankpressi, O.knutei, O.packardorum, O.roseus and O.talkovici. We also provided additional DNA sequences from previously reported localities for two species: Osedaxpriapus and O.randyi. To assess the distribution of each species, we used cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) sequences to generate haplotype networks and assess connectivity amongst localities where sampling permitted. Osedaxfrankpressi, O.packardorum, O.priapus, O.roseus and O.talkovici all had one or more dominant COI haplotypes shared by individuals at multiple localities, suggesting high connectivity throughout some or all of their ranges. Low ΦST values amongst populations for O.packardorum, O.roseus and O.talkovici confirmed high levels of gene flow throughout their known ranges. High ΦST values for O.frankpressi between the eastern Pacific and the Brazilian Atlantic showed little gene flow, reflected by the haplotype network, which had distinct Pacific and Atlantic haplotype clusters. This study greatly expands the ranges and provides insights into the phylogeography for these nine species.
Keywords: COI; deep-sea; invertebrates; phylogeography; polychaetes; range extension; whale-falls.
Gabriella H. Berman, Shannon B. Johnson, Charlotte A. Seid, Robert C. Vrijenhoek, Greg W. Rouse.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest to declare Disclaimer: This article is (co-)authored by any of the Editors-in-Chief, Managing Editors or their deputies in this journal.
Figures

References
-
- Barroso Romulo, Klautau Michelle, Solé-Cava Antonio M., Paiva Paulo C. Eurythoecomplanata (Polychaeta: Amphinomidae), the ‘cosmopolitan’ fireworm, consists of at least three cryptic species. Marine Biology. 2009;157(1):69–80. doi: 10.1007/s00227-009-1296-9. - DOI
-
- Cowart Dominique A., Huang Chunya, Arnaud-Haond Sophie, Carney Susan L., Fisher Charles R., Schaeffer Stephen W. Restriction to large-scale gene flow vs. regional panmixia among cold seep Escarpia spp. (Polychaeta, Siboglinidae) Molecular Ecology. 2013;22(16):4147–4162. doi: 10.1111/mec.12379. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coykendall D Katharine, Johnson Shannon B, Karl Stephen A, Lutz Richard A, Vrijenhoek Robert C. Genetic diversity and demographic instability in Riftiapachyptila tubeworms from eastern Pacific hydrothermal vents. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 2011;11(1) doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-96. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eilertsen Mari H., Georgieva Magdalena N., Kongsrud Jon A., Linse Katrin, Wiklund Helena, Glover Adrian G., Rapp Hans T. Genetic connectivity from the Arctic to the Antarctic: Sclerolinumcontortum and Nicomachelokii (Annelida) are both widespread in reducing environments. Scientific Reports. 2018;8(1):1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23076-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
