Defining the threshold: triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio's non-linear impact on tubular atrophy in primary membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 38327562
- PMCID: PMC10847559
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1322646
Defining the threshold: triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio's non-linear impact on tubular atrophy in primary membranous nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Hyperlipidemia is common in primary membranous nephropathy (PMN) patients, and tubular atrophy (TA) is an unfavorable prognostic factor. However, the correlation between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio and TA is controversial. Therefore, our study aimed to investigate the association between the TG/HDL-C ratio and TA in PMN patients.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study and collected data from 363 PMN patients at Shenzhen Second People's Hospital from January 2008 to April 2023. The primary objective was to evaluate the independent correlation between the TG/HDL-C ratio and TA using binary logistic regression model. We used a generalized additive model along with smooth curve fitting and multiple sensitivity analyses to explore the relationship between these variables. Additionally, subgroup analyses were conducted to delve deeper into the results.
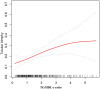
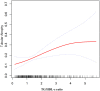
Results: Of the 363 PMN patients, 75 had TA (20.66%). The study population had a mean age of 46.598 ± 14.462 years, with 217 (59.78%) being male. After adjusting for sex, age, BMI, hypertension, history of diabetes, smoking, alcohol consumption, UPRO, eGFR, HB, FPG, and ALB, we found that the TG/HDL-C ratio was an independent risk factor for TA in PMN patients (OR=1.29, 95% CI: 1.04, 1.61, P=0.0213). A non-linear correlation was observed between the TG/HDL-C ratio and TA, with an inflection point at 4.25. The odds ratios (OR) on the left and right sides of this inflection point were 1.56 (95% CI: 1.17, 2.07) and 0.25 (95% CI: 0.04, 1.54), respectively. Sensitivity analysis confirmed these results. Subgroup analysis showed a consistent association between the TG/HDL-C ratio and TA, implying that factors such as gender, BMI, age, UPRO, ALB, hypertension and severe nephrotic syndrome had negligible effects on the link between the TG/HDL-C ratio and TA.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates a non-linear positive correlation between the TG/HDL-C ratio and the risk of TA in PMN patients, independent of other factors. Specifically, the association is more pronounced when the ratio falls below 4.25. Based on our findings, it would be advisable to decrease the TG/HDL-C ratio below the inflection point in PMN patients as part of treatment strategies.
Keywords: cross-sectional study; non-linear; primary membranous nephropathy; triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio; tubular atrophy.
Copyright © 2024 Guan, Wu, Cheng, Qi, Chen, Song, Hu and Wan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association between triglyceride-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and prediabetes: a cross-sectional study in Chinese non-obese people with a normal range of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.J Transl Med. 2022 Oct 22;20(1):484. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03684-1. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36273126 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride-to-high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and three-month outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke: a second analysis based on a prospective cohort study.BMC Neurol. 2022 Jul 16;22(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02791-2. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35842590 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and incident of diabetes mellitus: a secondary retrospective analysis based on a Chinese cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Mar 4;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01213-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32131838 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio and arterial stiffness in Japanese population: a secondary analysis based on a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 May 29;17(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0776-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29843793 Free PMC article.
-
The Triglyceride/HDL Ratio as a Surrogate Biomarker for Insulin Resistance.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 5;12(7):1493. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071493. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors and predictive model for renal outcomes in autoimmune membranous nephropathy with and without acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study.PeerJ. 2025 Apr 16;13:e19331. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19331. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40256734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mariani LH, Martini S, Barisoni L, Canetta PA, Troost JP, Hodgin JB, et al. . Interstitial fibrosis scored on whole-slide digital imaging of kidney biopsies is a predictor of outcome in proteinuric glomerulopathies. Nephrol Dial Transplant (2018) 33:310–18. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw443 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

