Expanded specific T cells to hypomutated regions of the SARS-CoV-2 using mRNA electroporated antigen-presenting cells
- PMID: 38327807
- PMCID: PMC10847775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101192
Expanded specific T cells to hypomutated regions of the SARS-CoV-2 using mRNA electroporated antigen-presenting cells
Abstract
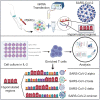
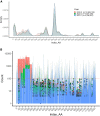
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused about seven million deaths worldwide. Preventative vaccines have been developed including Spike gp mRNA-based vaccines that provide protection to immunocompetent patients. However, patients with primary immunodeficiencies, patients with cancer, or hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients are not able to mount robust immune responses against current vaccine approaches. We propose to target structural SARS-CoV-2 antigens (i.e., Spike gp, Membrane, Nucleocapsid, and Envelope) using circulating human antigen-presenting cells electroporated with full length SARS-CoV-2 structural protein-encoding mRNAs to activate and expand specific T cells. Based on the Th1-type cytokine and cytolytic enzyme secretion upon antigen rechallenge, we were able to generate SARS-CoV-2 specific T cells in up to 70% of unexposed unvaccinated healthy donors (HDs) after 3 subsequent stimulations and in 100% of recovered patients (RPs) after 2 stimulations. By means of SARS-CoV-2 specific TCRβ repertoire analysis, T cells specific to Spike gp-derived hypomutated regions were identified in HDs and RPs despite viral genomic evolution. Hence, we demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-loaded antigen-presenting cells are effective activating and expanding COVID19-specific T cells. This approach represents an alternative to patients who are not able to mount adaptive immune responses to current COVID-19 vaccines with potential protection across new variants that have conserved genetic regions.
Keywords: RNA-based immunotherapy; SARS-CoV-2; adoptive T cells; antigen-presenting cells; hypomutated regions.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The disclosures from D.A.M. are as follows: holds patented technologies that have been licensed or have exclusive options to license to Celldex Therapeutics, Annias, Immunomic Therapeutics, and iOncologi; receives research funding from Immunomic Therapeutics; he is also the cofounder of iOncologi, Inc., an immuno-oncology biotechnology company. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. E.O.R., V.T., F.P.G., C.Y., H.M.G, P.C, E.J.S, and D.A.M. have patents on mRNA technologies for COVID-19 and related to cellular therapy methods for viral vaccines.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Specific immune response to mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 in patients receiving allogeneic stem cell transplantation for myeloid malignancy was altered by immunosuppressive therapy.Leuk Res. 2023 Jul;130:107314. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2023.107314. Epub 2023 May 16. Leuk Res. 2023. PMID: 37216792 Free PMC article.
-
Off-the-Shelf Partial HLA Matching SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Specific T Cell Therapy: A New Possibility for COVID-19 Treatment.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 23;12:751869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.751869. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003063 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Immunity Shifts the Fc-Effector Quality of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine-Induced Immunity.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0164722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01647-22. Epub 2022 Aug 24. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36000735 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Pandemic and Vaccines Update on Challenges and Resolutions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Sep 10;11:690621. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.690621. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34568087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Next Generation Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern.Viruses. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):624. doi: 10.3390/v15030624. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA aggregates harness the danger response for potent cancer immunotherapy.Cell. 2024 May 9;187(10):2521-2535.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.04.003. Epub 2024 May 1. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38697107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University; 2020. Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at the.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

